What is default gateway
When a computer in your Local Area Network (LAN) wants to communicate with a computer on a remote network, the data packets need to traverse through the router. Default gateway IP address is the IP address of the interface of the router that is facing the Local Area Network (LAN). The default gateway IP address must configured on the TCP/IP settings of all the devices on that LAN to succesfully communicate with remote networks. All the data packets destined to any other network must be forwarded to default gateway.
Please refer below image to see an example.
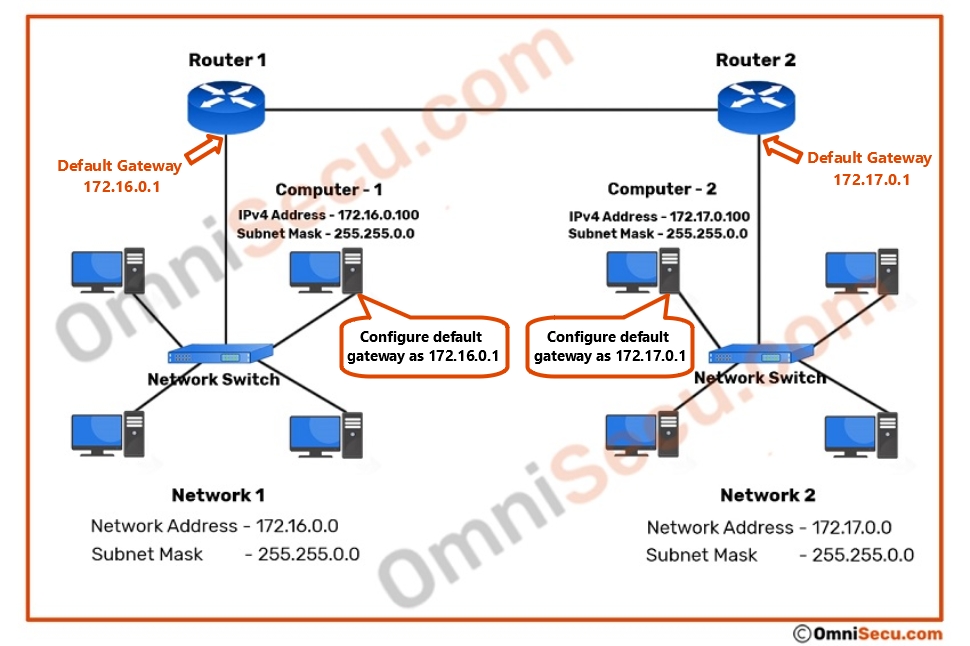
From above image, we can see that the default gateway IP address of "Network 1" is 172.16.0.1 255.255.0.0, which belongs to 172.16.0.0 255.255.0.0 network. The default gateway IP address of "Network 2" is 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0, which belongs to 172.17.0.0 255.255.0.0 network. So, the most important fact to note here is that a computer’s IP address and its configured default gateway IP address must be in the same network.
How default gateway works
Consider "Computer-1" from Network 1 (172.16.0.0 255.255.0.0 network) wants to communicate with "Computer-2" located in Network 2 (172.17.0.0 255.255.0.0 network) using TCP/IP protocol suite. "Computer-1" performs a comparison process using its own IPv4 address and subnet mask, with the destination IPv4 address.
Refer two images below. First images contains the source IPv4 address, subnet mask and the destination IPv4 address in decimals. Second image contains the source IPv4 address, subnet mask and the destination IPv4 address in binaries.
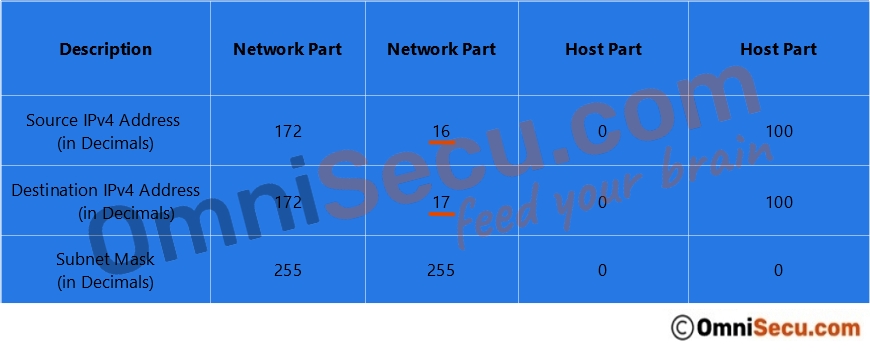
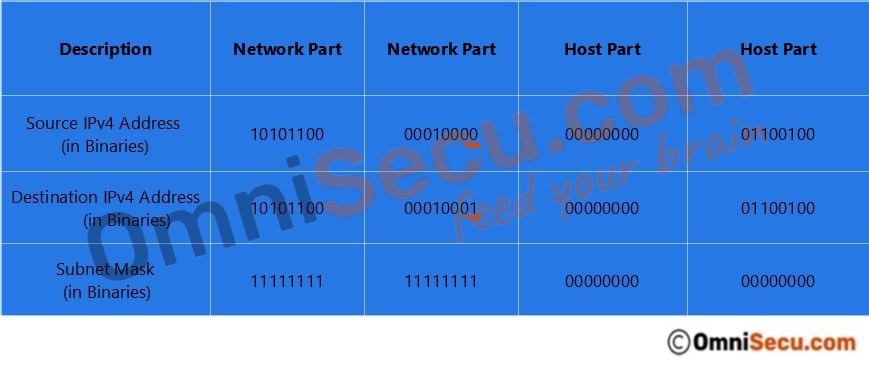
You can see from above images that the network part of the source IPv4 address and the destination IPv4 address are not the same. The meaning is that the source network and the destination network are different. In this case, the destination IPv4 address is located in a remote network and the data packet must be forwarded to default gateway to reach the destination network.
If the destination IPv4 address is located in a remote network, the computer needs to handover the data packet to the default gateway. Every computer is configured with the IP address of default gateway in its TCP/IP settings (see below). Now the computer resolves the MAC address of the default gateway (using Address Resolution Prorocol (ARP)), encapsulates the IPv4 packet in an Ethernet Frame with destination MAC address as the MAC address of the default gateway and forward the packet to the network switch. Network switch will then deliver the packet to the default gateway. Once the data packet is handed over to the router, then it the responsibility of the router to forward the packet to the correct destination network.
How to find default gateway IP address in TCP/IP settings
To view the default gateway IPv4 address configured on your Windows Operating System based computer’s TCP/IP settings, follow these steps.
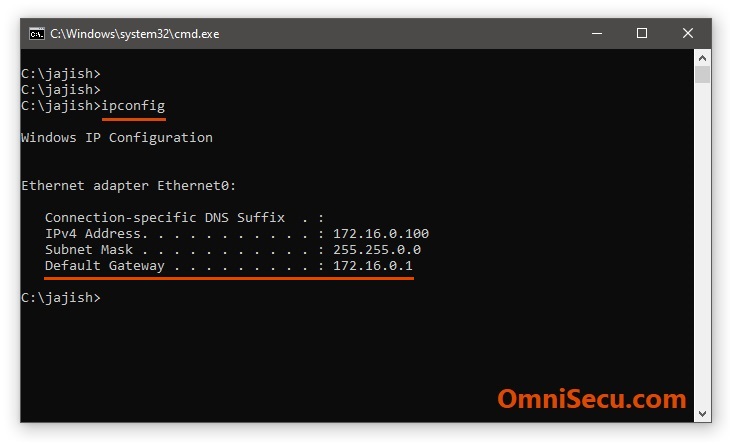
Run command prompt by right-clicking Start > Run > type cmd and then clicking "OK".
Type the command "ipconfig" in the prompt and Enter. Do remember to remove double quotes.