What are private IP addresses - RFC 1918 private addresses
Private IP addresses (RFC 1918 addresses) are used to conserve IPv4 addresses from depletion by reserving ranges of IPv4 addresses for the devices which are inside a private network. A private network is a network which is not directly connected to the internet.
IPv4 started its journey in networking and in internet long back in early 1970's. It was a project for DARPA (Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency) during the early development of computers and other network devices. During that time, there were only a few computers all over the world and the networking gurus of those period decided to give a 32-bit binary number as IPv4 address for the network devices. The 32-bit IPv4 address provides 4,294,967,296 unique IPv4 addresses and it was a huge addressing scheme of that period.
The problems related with 32-bit IPv4 addresses started in 1990's with the rapid development of the Internet. Internet spread all over the world and millions of computers became part of the internet. The main problem related with IPv4 addresses was 32-bit IPv4 addresses were not enough to provide addressing for large number of devices in the internet.
In real network environment, many devices which are inside a private network (Example - a Local Area Network (LAN) inside a company, a Local Area Network (LAN) inside organization or a home network) do not need to communicate with any device outside its own Local Area Network (LAN). Even the computers inside a private network need to connect internet, there is no need of direct connectivity, they are connected to the internet via a router or any other end-point device. The idea of Network Address Translation (NAT) arose from the above reality. Following image shows the concept of Network Address Translation (NAT).
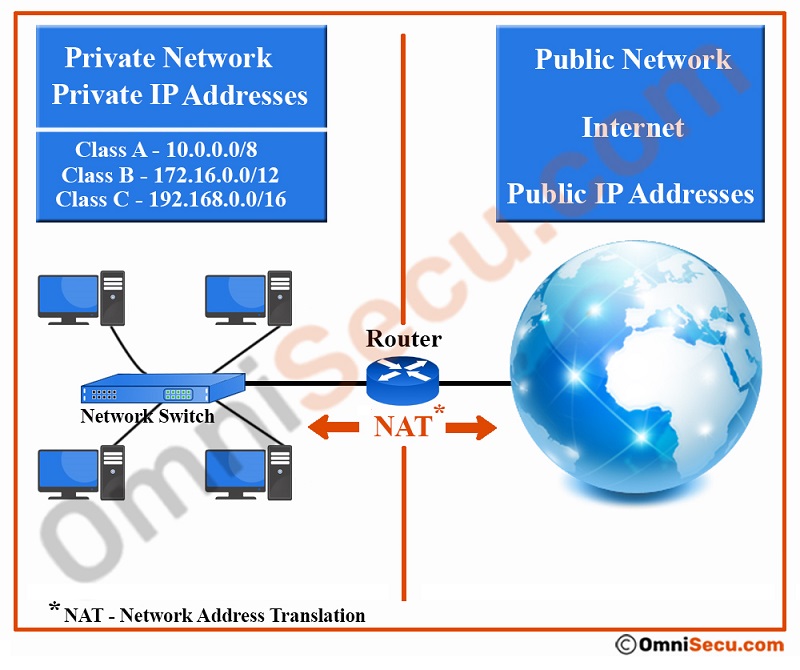
The idea of Private IPv4 addresses (defined by RFC 1918, and also known as RFC 1918 IPv4 addresses) was to reserve IPv4 addresses for the devices which are inside a private network (Example - a Local Area Network (LAN) inside a company, a Local Area Network (LAN) inside organization or a home network).
IPv4 datagrams originating or destined to these private networks (configured with a private IPv4 address) are dropped by public internet routers.
The end-point device in a private network (usually a router or a firewall) translates these IP addresses to a public IPv4 address and forwarded to internet, when the IPv4 datagram leaves the network to the public outside internet. The public IPv4 addresses are translated back to private IPv4 addresses and forwarded to the private inside network when an IPv4 packet arrived at the end-point device (usually a router or a firewall) of a private network.
One network interface of the end-point device (usually a router or a firewall) is connected to the inside private network and configured with a private IPv4 address and other network interface is connected to the public internet via a Service Provider and assigned with public IPv4 addresses.
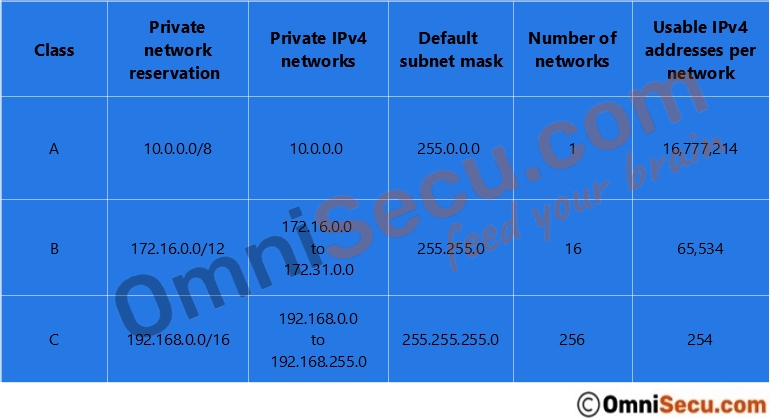
The following IPv4 address ranges are reserved for private networks (Example - a Local Area Network (LAN) inside a company, a Local Area Network (LAN) inside organization or a home network).
• In Class A, 10.0.0.0/8 prefix range.
Class A private IPv4 addresses starts from 10.0.0.0 to 10.255.255.255. 10.0.0.0/8 is the network IPv4 address and10.255.255.255 is the directed broadcast IPv4 address.
Consists of total 16,777,216 IPv4 Addresses (16,777,214 usable IPv4 addresses). Class A range of private IPv4 addresses are used for large network which need a bigger pool IPv4 addresses.
• In Class B, 172.16.0.0/12 prefix range.
Class B private IPv4 addresses starts from 172.16.0.0 to 172.31.255.255. 172.16.0.0 is the network IPv4 address for 172.16.0.0/16 network and 172.31.255.255 is the is the directed broadcast IPv4 address for 172.31.0.0/16 network.
Consists of total 1,048,576 IPv4 Addresses (1,048,544 usable IPv4 addresses). Class B range of private IPv4 addresses are used for medium-sized network.
• In Class C network 192.168.0.0/16 prefix range
Class C private IPv4 addresses Starts from 192.168.0.0 to 192.168.255.255. 192.168.0.0 is the network IPv4 address of 192.168.0.0/24 network and 192.168.255.255 is the directed broadcast IPv4 address for 192.168.255.0/24 network.
Consists of total 65,536 IPv4 Addresses (65,024 usable IPv4 addresses). Class C range of private IPv4 addresses are used for small networks.
Please refer below table, which shows summary of private IP address reservations.