Unique Local IPv6 Addresses
IPv6 unique local addresses are the addresses which can be used inside an enterprise company at multiple sites. IPv6 unique local Addresses are defined in IETF RFC 4193 and reserved with a range of FC00::/7. A range of FC00::/7 means that IPv6 unique local addresses begin with 7 bits with exact binary pattern as 1111 110L.
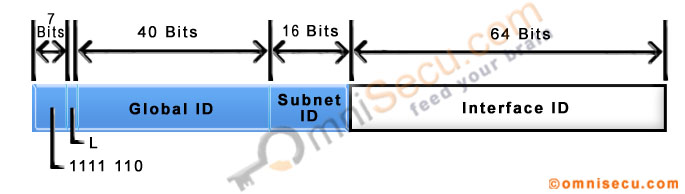
If the value of single binary bit "L" is set to 1, the unique local IPv6 multicast address is locally assigned. The value 0 may be defined in the future. So, we can have two unique local IPv6 Unicast Address prefixes. 1111 1100 (FC in hexadecimals) and 1111 1101 (FD in hexadecimals). Unique local IPv6 multicast addresses starting with FD (L binary bit set to 1) are locally assigned.
Refer Unique Local IPv6 Unicast Addresses RFC for more details.
IETF RFC 4193 describes unique local addresses as IPv6 unicast address format that is globally unique and is intended for IPV6 local communications. IPv6 unique local addressess are not expected to be routable on the Internet, but IPv6 unique local addressess are routable inside of a company’s multiple sites.
Like Global Unicast IPv6 addresses, unique local addresses also have a global scope. But the scope of unique local addresses are defined by organizations by routing topology and filtering policies at the site boundary level. The well-known prefix of IPv6 unique local addresses can be used for filtering the inbound and outbound IPv6 traffic with unique local source and destination addresses at site level. DNS entries for unique local IPv6 Addresses are not created in public Internet DNS.
Unique local IPv6 addresses can be viewd as globally unique "private routable" IPv6 addresses, which are typically used inside an organization.
Written by Jajish Thomas. Last updated on 17th May, 2024.