Multicast IPv6 Address Format, Prefix, Flags and Scope
IPv6 multicast communication is similar to IPv4 multicast communication. IPv6 devices can join and listen for multicast traffic on an IPv6 multicast address. An IPv6 multicast address identifies multiple interfaces. In IPv6 multicast type of communication, IPv6 datagram packets addressed to an IPv6 multicast address are delivered to all interfaces that are identified by that IPv6 multicast address.
IPv6 devices can join or leave a multicast group at any time and IPv6 nodes can join and listen to multiple IPv6 multicast addresses at the same time.
Following image shows the IPv6 multicast address format.
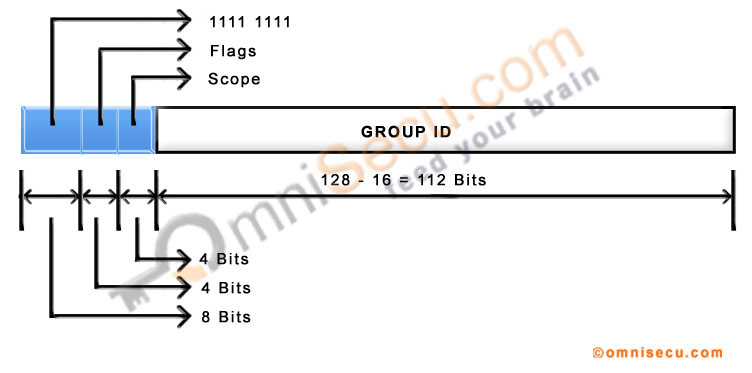
• For IPv6 multicast addresses, the first eight bits are reserved as 1111 1111. Thus, the prefix of an IPv6 multicast address is ff00::/8. Similar to IPv6 link-local addresses, it is easy to identify an IPv6 multicast address, because IPv6 multicast addresses have left most hexadecimal digits as "FF"
• After the leftmost 8 bits which are reserved as "1111 1111", the next four bits are known as flags. Only 3 of the 4 flag bits in the flags field are defined currently. The most significant bit in the 4 bits flags field is reserved for future use. The remaining three flags are known as R, P and T.
| 4 Bits inside flags field | Flag name | When "0" set | When "1" set |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 (Most Significant Bit) | Currently not in use | Currently not in use | Currently not in use |
| 1 | R (Rendezvous) | When R flag set to 0, the multicast rendezvous point is not embedded with multicast address | When R flag set to 1, the multicast rendezvous point is embedded with multicast address |
| 2 | P (Prefix) | When P flag set to 0, the multicast address is not based on network prefix | When P flag set to 1, the multicast address based on network prefix |
| 3 (Least Significant Bit) | T (Transient) | When T flag set to 0, the multicast address is a permanently assigned (well-known) multicast IPv6 address |
When T flag set to 1, the multicast address is a transient (Dynamically assigned) multicast address |
• After the leftmost 8 bits which are reserved as "1111 1111", and the next four flag bits, the next four bits are defined as the Scope bits. Scope bits (4 bits) are used to indicate the scope of delivery of IPv6 multicast traffic.
The following table lists the values possible currently for the scope field.
| Value |
Scope | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | Reserved | Currently not in use |
| 1 | Interface-local scope | The Interface-local scope is limited for a local single interface only. Useful only for loopback delivery of multicasts within a node. |
| 2 | Link-local scope | Link-local scope is defined for the local link. The traffic with the multicast address of FF02::2 is limited to local link scope. An IPv6 router will never forward the multicast traffic destined to FF02::2 beyond the local link. |
| 3 | Subnet-local scope | Subnet-local scope ranges subnets on multiple links. |
| 4 | Admin-local scope | Administratively configured scope. Definition states that "the smallest scope that must be administratively configured". |
| 5 | Site-local scope | The scope of Site-local multicast addresses are within the local physical network. For example, a small branch office. Site-local Multicast packets will not cross the IPv6 border router at the site. |
| 8 | Organization-local scope | The scope of Organization-local addresses are within different sites inside an organization. Organization-Local Multicast packets will not cross the organization’s IPv6 border router to reach the IPv6 public internet. |
| E | Global scope | Scope is the Global IPv6 internet. |
| F | Reserved | Currently not in use. |
• The next 112 bits Group ID is used to identify the multicast group within the given scope (either permanent or transient).
Most important link-local scope IPv6 multicast addresses are listed below.
| Important IPv6 Link-local scope Multicast Addresses | Description |
|---|---|
| FF02::1 | All Nodes IPv6 multicast address. All IPv6 nodes in same link will listen to FF02::1 IPv6 multicast address. |
| FF02::2 | All Routers IPv6 multicast address. All IPv6 routers on the same link will listen to FF02::2 IPv6 multicast address. |
| FF02::4 | The all-Distance Vector Multicast Routing Protocol (DVMRP) routers address. Used to reach all DVMRP multicast routers on the same link. |
| FF02::5 | OSPF IPv6 multicast address. (Remember, in IPv4, OSPF multicast address was 224.0.0.5) |
| FF02::6 | OSPFv3 Designated Router’s IPv6 multicast address. (Remember, in IPv4, OSPF Designated Router's (DR) multicast address was 224.0.0.6). Only DR and BDR listen to FF02::6 multicast IPv6 address. |
| FF02::9 | RIPng IPv6 multicast address. (Remember, in IPv4, RIPv2 multicast address was 224.0.0.9) |
| FF02::A | EIGRP IPv6 multicast address. (Remember in IPv4, EIGRP multicast address was 224.0.0.10. A is the hexadecimal equivalent of decimal 10) |
| FF02::D | All PIM Routers |
| FF02::16 | All MLDv2-capable routers |
| FF02::1:2 | DHCPv6 Servers and DHCPv6 Relay Agents |
| FF02::1:FF00:0000/104 | Solicited-Node IPv6 Multicast address |
Written by Jajish Thomas. Last updated on 17th May, 2024.