Router Solicitation (RS) and Router Advertisement (RA) Messages in IPv6
What is Router Discovery (RD)
NDP (Neighbor Discovery Protocol) is a part of ICMPv6 (Internet Control Message Protocol version 6). Router Discovery (RD) in IPv6 is a sub-part of NDP (Neighbor Discovery Protocol). Router Discovery (RD) allows the IPv6 devices in a network to contact IPv6 routers to gather the relevant network information (Default Gateway IPv6 address, Default Gateway IPv6 address Prefix and Prefix Length etc.) for internetwork communication.
When an IPv6 enabled computer boots up in a network, and if that computer is not configured with a Default Gateway IPv6 address (IPv6 address of the Router’s connected interface) configured, Router Discovery (RD) allows it to find the router and collect the required Default Gateway IPv6 address and other router related parameters.

Router Solicitation (RS) and Router Advertisement (RA) Messages
There are two main types of ICMPv6 Messages related with Router Discovery (RD) in IPv6. One is Router Solicitation (RS) Message and the other is Router Advertisement (RA) Message. Router Solicitation (RS) Messages are sent by the hosts on the network to find routers on an IPv6 network. Router Advertisement (RA) Messages are sent by routers to hosts to inform about the Default Gateway IPv6 address and other router related parameters. IPv6 network hosts can learn about the presence of routers in the network, upon receiving Router Advertisement (RA) Messages from the routers.
Router Solicitation (RS) and Router Advertisement (RA) Messages, which are the part of ICMPv6 Messages are used for Router Discovery (RD) functionalities. Router Solicitation (RS) and Router Advertisement (RA) Messages are defined in RFC 4861. Please refer the following lesson to know more about different types of messages in ICMP6, Multicast type of network communication is used for sending Router Solicitation (RS) Messages.
Exploring Router Solicitation (RS) Message
Following table explains about Router Solicitation (RS) Message in detail.
| Type of ICMPv6 Message | Send by | Send to | Type of communication | Destination IPv6 address | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Router Solicitation | IPv6 capable devices (except routers) | All IPv6 routing capable devices in the network | Multicast | FF02::2 (all-routers Multicast address) | Router Solicitation (RS) Messages are sent by IPv6 capable devices to identify IPv6 capable routers on the network. The purpose is to get the Default Gateway address and other network related parameters from the IPv6 routers in the network. |
The format for Router Solicitation (RS) Message is defined in RFC 4861. The format for a Router Solicitation (RS) Message is based on a normal ICMPv6 message format.
Following image shows the format for Router Solicitation (RS) Message.
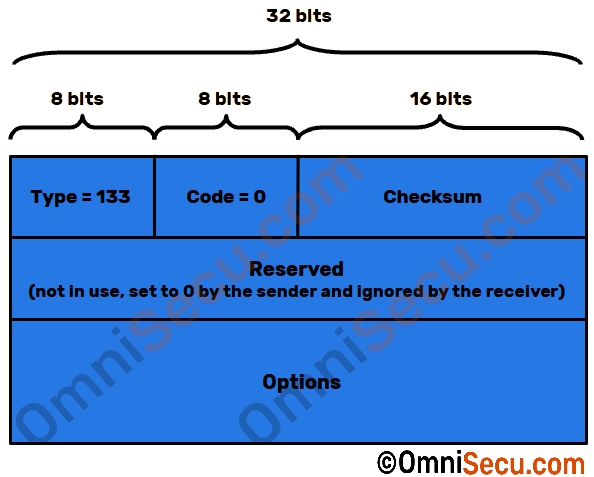
Router Solicitation (RS) Message fields are explained in below table.
| Field | Size | Description | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Type | 8 bits | Type field value denots the type of the ICMPv6 message. Type field value for a Router Solicitation (RS) is 133. | 133 |
| Code | 8 bits | Code field provides further classification of this ICMPv6 message. Code field value is 0 for a Router Solicitation (RS) Message. | 0 |
| Checksum | 16 bits | Checksum value | |
| Reserved | 32 bits | Reserved field | Currently 0 |
| Options | Variable | Contains optional values. | Contains optional values. For example; Source link-layer address. |
Following image is a screenshot of Wireshark capture of a Router Solicitation (RS) Message.
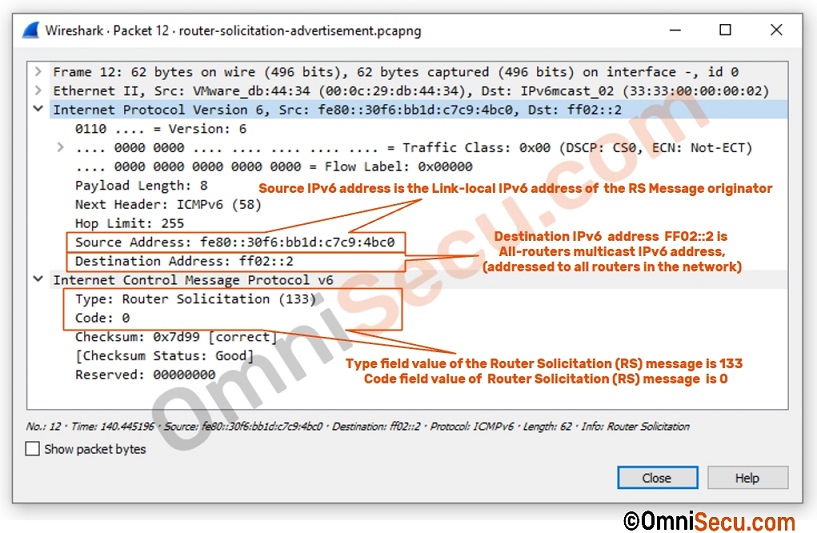
As you can see from the above capture screenshot, source IPv6 address is the Link-local IPv6 address of the RS Message originator. Destination IPv6 address FF02::2 is All-routers multicast IPv6 address (addressed to all routers in the local segment). We had already discussed that the Type field value of Router Solicitation (RS) ICMPv6 Message is 133 and Code field value of Router Solicitation (RS) message is 0.
Exploring Router Advertisement (RA) Message
Following table explains about Router Advertisement (RA) Message in detail. Two types of Router Advertisement (RA) Messages are Solicited Router Advertisement Message and Unsolicited Router Advertisement Message.
| Type of ICMPv6 Message | Send by | Send to | Type of communication | Destination IPv6 address | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Solicited Router Advertisement Messages | Routers | As reply for a Router Solicitation (RS) Message | Multicast | FF02::1 (all-nodes Multicast address) | Solicited Router Advertisement (RA) Messages are sent by a router as a response, when an IPv6 device sends a Router Solicitation (RS) Message to routers, to obtain Default Gateway IPv6 address and other router related parameters. |
| Unsolicited Router Advertisement Messages | Routers | To all IPv6 hosts periodically | Multicast | FF02::1 (all-nodes Multicast address) | Unsolicited Router Advertisement (RA) Messages and send periodically to all network devices to advertise the presence of routers. |
The format for Router Advertisement (RA) Message is defined in RFC 4861. The format for a Router Advertisement (RA) Message is different than a normal ICMPv6 message format.
Following image shows the format for Router Advertisement (RA) Message.
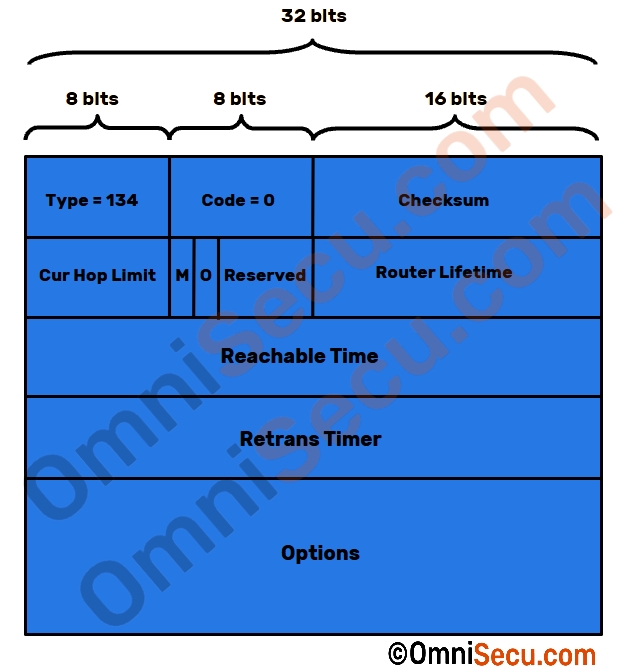
Router Advertisement (RA) Message fields are explained in below table.
| Field | Size | Description | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Type | 8 bits | Type field value denotes the type of the ICMPv6 message. Type field value for a Router Advertisement (RA) Message is 134. | 133 |
| Code | 8 bits | Code field provides further classification of this ICMPv6 message. Code field value is 0 for a Router Advertisement (RA) Message. | 0 |
| Checksum | 16 bits | Checksum value | 0 |
| Cur Hop Limit | 8 bits | The default value that the router recommending to devices, that should be placed in the Hop Count field of the IPv6 header for outgoing IPv6 packets. If 0, the router is not recommending a Hop Limit value in this Router Advertisement. | |
| M | 1 bit | "Managed address configuration" flag | 0 or 1 |
| O | 1 bit | "Other configuration" flag | 0 or 1 |
| Reserved | 6 bits | Reserved and currently unused | 0 |
| Router Lifetime | 16 bit | A Lifetime value of 0 is used to indicate that the router is not a default router and should not appear on the default router list. | |
| Reachable Time | 32 bits | The time in milliseconds that a node assumes a neighbor is reachable after having received a reachability confirmation. If this field has a value of 0, the reachable time is unspecified by the router. | |
| Retrans Timer | 32 bits | The time in milliseconds, between retransmitted Neighbor Solicitation Messages. if this field has a value of 0, The Retrans time is unspecified by the router. | |
| Options | variable | Message body contains options like Source link-layer address, MTU, Prefix Information. |
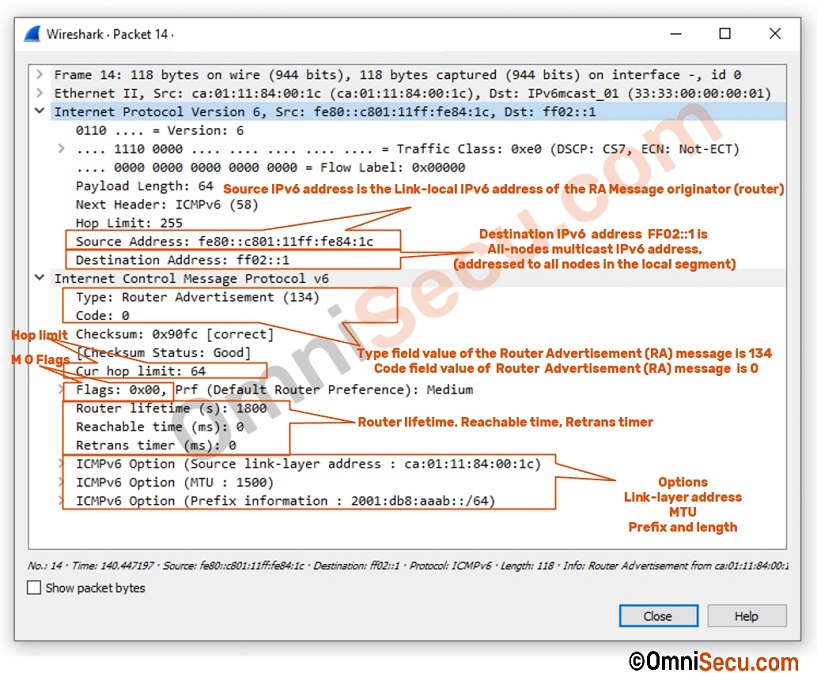
Following image is a screenshot of Wireshark capture of a Router Advertisement (RA) Message.
How Router Discovery (RD) works in IPv6 using Router Solicitation (RS) and Router Advertisement (RA) Messages
A simple explanation for a Router Solicitation (RS) Message is that, it is the message from an IPv6 device asking to all the routers present in the network "Any router up and running IPv6 routing there? If anyone there, please respond me back".
Router Advertisement (RA) Message is the reply from a router for a Router Solicitation (RS) message sent by an IPv6 device. An easy explanation for Router Advertisement (RA) Message sent from a router to a network device is that "I am the router running IPv6 routing here. Please note my IPv6 address, prefix, prefix length and some other parameters required for you to participate our internetwork."
Router Solicitation (RS) Messages are sent to IPv6 all-routers Multicast address FF02::2. Only routers listen to the IPv6 multicast messages addressed to FF02::2. Multicast Router Solicitation (RS) Messages sent to FF02::2 are only for the routers in the network. All non-router IPv6 devices discard messages addressed to FF02::2 for better resource utilization, because those messages are meaningless to them.
Please remember that there are two types of Router Advertisement (RA) Messages, Solicited Router Advertisement Message and Unsolicited Router Advertisement Message. Unsolicited Router Advertisement Messages are sent voluntarily by IPv6 routers, periodically, not as a reply for a Router Solicitation (RS) Message. Both Solicited Router Advertisement Message and Unsolicited Router Advertisement Message are explained in another section above.
Following steps explain how Router Discovery (RD) works in IPv6. Please refer the following image.
Step 1 - Desktop computer PC 1 is just booting up. PC 1 needs to locate the routers running IPv6 routing in its network to get Default Gateway IPv6 address and other related network parameters. To locate the routers running IPv6 routing in its network, PC 1 sends a Router Solicitation (RS) Message.
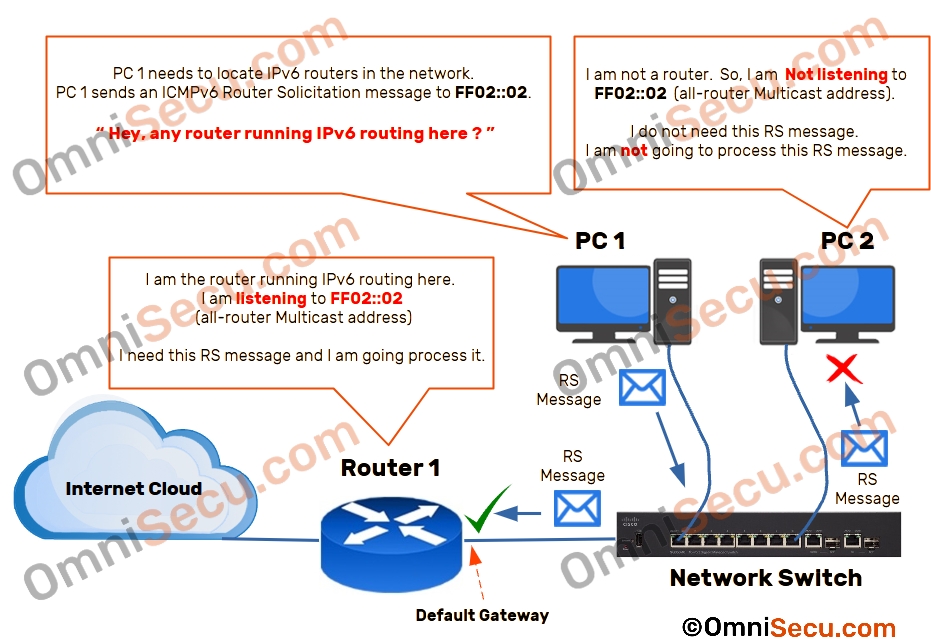
Step 2 - There are two other IPv6 devices in that network segment. A Desktop computer PC 2, and a router Router 1. Network Switch forwards that Router Solicitation (RS) Message to its connected ports. Both the Desktop computer PC 2, and the Router receive the Router Solicitation (RS) Message. The Router is listening to IPv6 Multicast IPv6 group address FF02::2, so it can process the Router Solicitation (RS) message. PC 2 is not listening to the IPv6 Multicast IPv6 group address FF02::2. PC 2 simply discards the Router Solicitation (RS) Message from PC 1, because Router Solicitation (RS) message is addressed to all-routers multicast address.
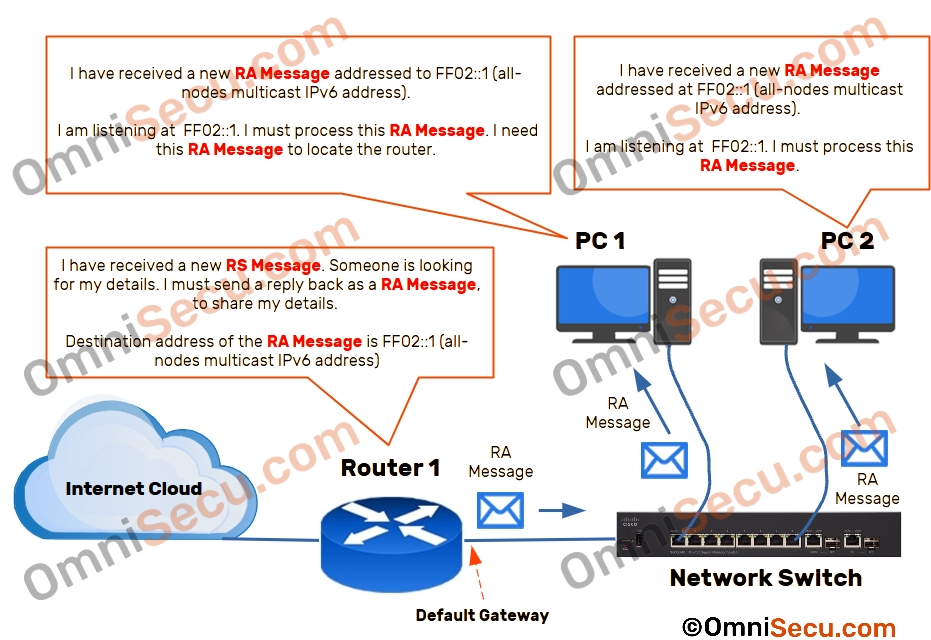
Step 3 - Once the Router 1 receives the Router Solicitation (RS) Message from PC 1, Router 1 can understand that an IPv6 device is trying to locate the router in its network segment. Now the router will prepare a Router Advertisement (RA) Message with the destination IPv6 address as FF02::1 (all-nodes multicast IPv6 address).
After receiving this Router Advertisement (RA) Message, the Desktop computer PC 1 can use the contents of this Router Advertisement (RA) Message to update it’s information related with the network router.
Written by Jajish Thomas. Last updated on 19th May, 2024.