NDP (Neighbour Discovery Protocol), functions of NDP, Neighbour Solicitation and Advertisement, Router Solicitation and Advertisement
Neighbor Discovery Protocol (NDP, defined in RFC 4861) is an important protocol in IPv6. Neighbor Discovery Protocol (NDP) is based on ICMPv6 and is used to identify the relationships between different neighboring devices in an IPv6 network. Many important functions of IPv6 like resolving MAC address of an IPv6 Address (in IPv4, ARP is used for this), Router Discovery etc., are now performed using Neighbor Discovery Protocol (NDP).
Following are the important functions of Neighbor Discovery Protocol (NDP).
• Discovering Routers Dynamically: Neighbor Discovery Protocol (NDP) is used to automatically discover routers in an IPv6 network using Router Solicitation & Router Advertisement messages.
• Discovering Network Prefixes Dynamically: Neighbor Discovery Protocol (NDP) is used to automatically discover IPv6 network prefixes where the host belongs to, by using Router Solicitaion & Router Advertisement messages.
• Resolving MAC address dynamically: We use IP addresses for communication but the addresses which are used by the LAN Switches for delivery of Ethernet frames to the destination devices are MAC addresses. In IPv4, Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) is used for resolving IPv4 address to MAC address. The role of Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) in IPv4 is performed by Neighbor Discovery Protocol (NDP) in IPv6.
• Autoconfiguration of IPv6 addresses: After learning IPv6 network prefixes using Neighbor Discovery Protocol (NDP) Router Solicitation & Router Advertisement messages, IPv6 devices can autoconfigure an IPv6 address by self generating the host part of the IPv6 address by using EUI–64 method.
• DAD (Duplicate Address Detection): DAD (Duplicate Address Detection) is a Neighbor Discovery Protocol (NDP) mechanism to detect whether duplicate IPv6 addresses exist in an IPv6 network. DAD (Duplicate Address Detection) is useful, because IPv6 has many address autoconfiguration mechanisms.
Neighbor Discovery Protocol (NDP) is based on ICMPv6 protocol. Following image shows Neighbor Discovery Protocol (NDP) encapsulation.
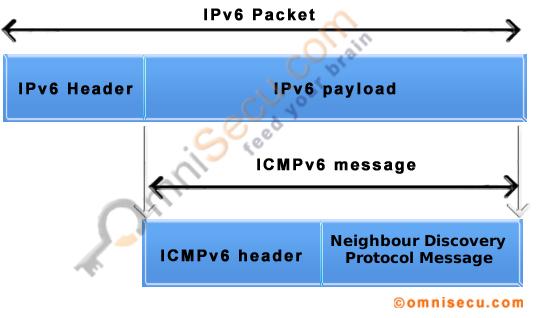
Neighbor Discovery Protocol (NDP) uses ICMPv6 Type field values from 133 to 137. Following table lists Neighbor Discovery Protocol (NDP) related ICMPv6 Type field values and their use.
| Sl. No | ICMPv6 Type Field Value |
Used for |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 133 | Router Solicitation message. Router Solicitation messages are requests to IPv6 Routers for Router Advertisement Messages. |
| 2 | 134 | Router Advertisement message. Router Advertisements are the NDP messages generated by IPv6 Routers to advertise their presence in the link and to inform other IPv6 devices in the link about important IPv6 link parameters like network prefix, prefix length, MTU etc. |
| 3 | 135 | Neighbor Solicitation message. Sent by an IPv6 device to resolve the link-layer address (MAC Address) of an IPv6 neighbor, to verify the reachability of cached link-layer address (MAC Address) and for Duplicate Address Detection (DAD). |
| 4 | 136 | Neighbor Advertisement message.Neighbor Advertisement messages are response to a Neighbor Solicitation message sent from an IPv6 neighbour. An IPv6 device can also send Unsolicited Neighbor Advertisement messages to announce a change in link-layer address. |
| 5 | 137 | Redirect message. Redirect messages are sent by IPv6 routers to inform IPv6 hosts in the link about a better next hop. |
Discovering Routers, Network Prefix and Prefix Length Dynamically using NDP Router Solicitation & Router Advertisement messages
As discussed before, IPv6 Neighbor Discovery Protocol (NDP) has many functions and one important function of IPv6 Neighbor Discovery Protocol (NDP) is Discovering IPv6 Routers "Dynamically". Neighbor Discovery Protocol (NDP) uses Router Solicitation and Router Advertisement messages (ICMPv6 Type Field Values 133 and 134 respectively) for discovering IPv6 Routers dynamically.
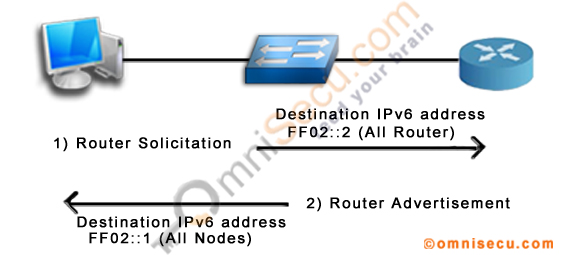
NDP (Neighbour Discovery Protocol) Router Solicitation
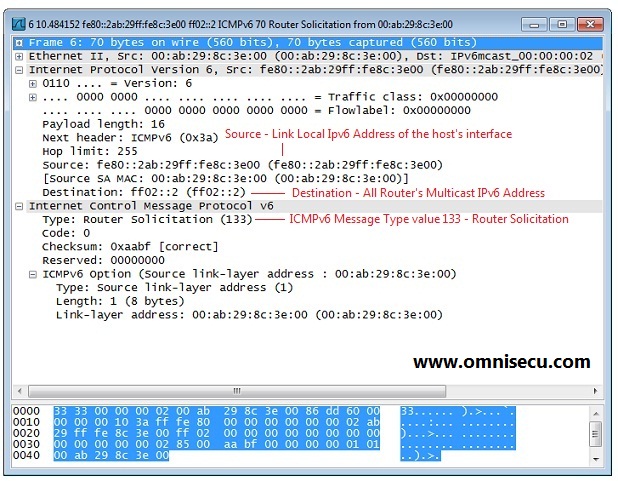
IPv6 hosts multicast (to a destination All router multicast IPv6 address FF02::2) an ICMPv6 message for the key IPv6 configuration information like Default Gateway, IPv6 Prefix and Prefix Length. The ICMPv6 message which the IPv6 hosts multicasts asking for Default Router, IPv6 Prefix and Prefix Length is called as the Router Solicitation (RS) message. ICMPv6 Type value for Router Solicitation message is 133.
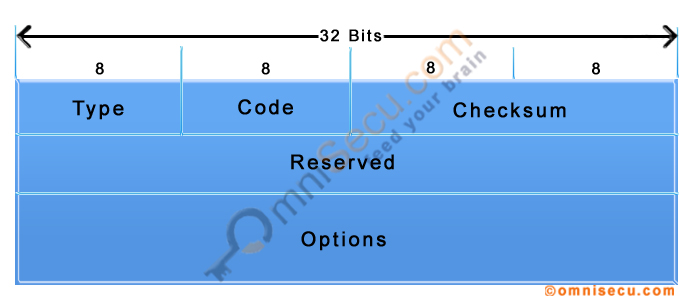
The format for NDP (Neighbour Discovery Protocol) Router Solicitation (RS) message is shown below.
Following screen shot is a Wireshark capture of NDP (Neighbour Discovery Protocol) Router Solicitation (RS) message.
Following table provides more information about NDP (Neighbour Discovery Protocol) Router Solicitation (RS) message fields.
| NDP Router Solicitation (RS) Message fields | Description |
|---|---|
| Type | The Type field in NDP (Neighbour Discovery Protocol) Router Solicitation (RS) message contains the Type value for Router Solicitation message, which is 133. |
| Code | The Code field in NDP (Neighbour Discovery Protocol) Router Solicitation (RS) message contains the Code value, which is 0 |
| Checksum | ICMPv6 checksum |
| Reserved | This field is reserved for future expansion and set to 0. |
| Source Link-Layer Address (ICMPv6 Option) | Source Link-Layer Address field in in NDP (Neighbour Discovery Protocol) Router Solicitation (RS) message contains the MAC address of the sender. This field is used by the IPv6 router to determine the unicast MAC address of the host who sent the Router Solicitation (RS) message. IPv6 Router will send back the Router Advertisement (RA) message as unicast to this MAC address. |
NDP (Neighbour Discovery Protocol) Router Advertisement
IPv6 routers reply back ICMPv6 Router Advertisement (RA) message (at a destination IPv6 all nodes multicast address FF02::1) in response to a Router Solicitation message from IPv6 hosts. The Router Advertisement (RA) message contains the key IPv6 configuration information like Default Router, IPv6 Prefix, Prefix Length, link MTU etc. ICMPv6 Type value for Router Advertisement message is 134.
Note that the IPv6 Routers send Router Advertisement (RA) messages periodically also, at a destination IPv6 all nodes multicast address FF02::1 to inform their presence.
The format for NDP (Neighbour Discovery Protocol) Router Advertisement (RA) message is shown below.
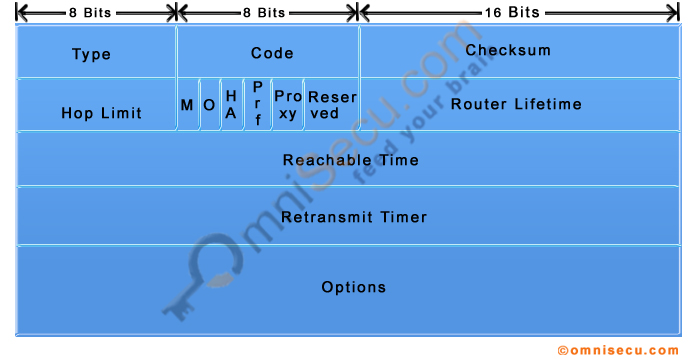
Following screen shot is a Wireshark capture of NDP (Neighbour Discovery Protocol) Router Advertisement (RA) message.
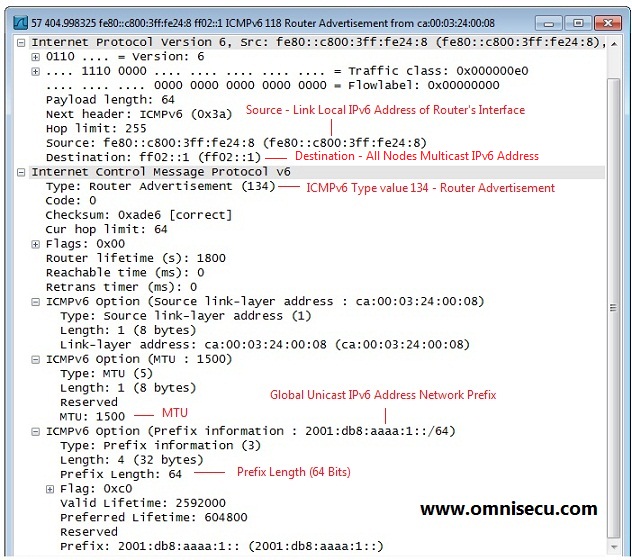
You can see from the above capture image that Router Advertisement (RA) message contains IPv6 Network Prefix, Prefix Length and Default Router Link Local Address.
Following table provides more information about NDP (Neighbour Discovery Protocol) Router Advertisement (RA) message fields.
| NDP Router Advertisement (RA) Message fields | Description |
|---|---|
| Type | The Type field in NDP (Neighbour Discovery Protocol) Router Advertisement (RA) message contains the Type value for Router Advertisement message, which is 134. |
| Code | The Code field in NDP (Neighbour Discovery Protocol) Router Advertisement (RA) message contains the Code value, which is 0 |
| Checksum | ICMPv6 checksum |
| Hop Limit | The Hop Limit field in in NDP (Neighbour Discovery Protocol) Router Advertisement (RA) message is the default value for Hop Limit, which the router is informing the hosts on the LAN to use as the Hop Limit for IPv6 datagrams they send. If the "Hop Limit" value is set to 0, the router is not informing a Hop Limit value to LAN hosts. |
| Flags (8 bits) | NDP (Neighbour Discovery Protocol) Router Advertisement (RA) message include some flag fields as described below. Managed Address Configuration flag: Managed Address Configuration flag is used to indicate the LAN hosts that the hosts must use an address configuration protocol like DHCPv6 to obtain addresses in addition to autoconfigured IPv6 addresses. Other Stateful Configuration flag: Other Stateful Configuration flag is used to indicate the LAN IPv6 hosts that they must use an address configuration protocol like DHCPv6 to obtain information other than addresses. Home Agent flag: Home Agent flag is used to indicate to hosts that the router acts as a Home Agent. Home agent is a router on the home network that maintains registrations of mobile hosts that are away from home. Default Router Preference: The Default Router Preference flag is used to indicate the level of preference for the advertising router if multiple routers advertise as default routers. Preference values is a two bit number with meaning as below. |
| Reserved | 2 bit field reserved for future expansion and set to 0. |
| Router Lifetime | Router Lifetime in NDP (Neighbour Discovery Protocol) Router Advertisement (RA) message is used to indicate the hosts in LAN receiving the NDP (Neighbour Discovery Protocol) Router Advertisement (RA) message that how long, the advertising router to be treated as the default router. This value is in seconds |
| Reachable Time | Reachable Time field in NDP (Neighbour Discovery Protocol) Router Advertisement (RA) message is used to inform the hosts in the LAN that how long they should consider a neighbor to be reachable after receiving a reachability confirmation. This value is in milliseconds. |
| Retransmission Timer | The Retransmission Timer field in NDP (Neighbour Discovery Protocol) Router Advertisement (RA) message indicates the amount of time between retransmissions of Neighbor Solicitation messages. This value is in milliseconds. |
| Source Link-Layer Address | Source Link-Layer Address field in NDP (Neighbour Discovery Protocol) Router Advertisement (RA) message contains the MAC address of the router interface which sent this Router Advertisement (RA) message. |
| MTU | The MTU field in NDP (Neighbour Discovery Protocol) Router Advertisement (RA) message contains the MTU of the link. |
| Prefix Information | The Prefix Information field in NDP (Neighbour Discovery Protocol) Router Advertisement (RA) message contains the IPv6 address network prefix and prefix length. |
Resolving Link-layer address (MAC address) dynamically using NDP Neighbour Solicitation (NS) and Neighbour Advertisement (NA) Messages
When an IPv6 device needs to discover the MAC address of corresponding IPv6 address of another interface in the Local Link, it sends the Neighbour Discovery Protocol (NDP) Neighbor Solicitation (NS) message. Neighbor Solicitation messages are sent to Solicited Node Multicast IPv6 Address and Neighbour Advertisement messages are Unicast (sent back to the Unicast Address of the interface which generated Neighbor Solicitation messages). ICMPv6 Type field values for Neighbor Solicitation and Neighbour Advertisement messages are 135 and 136 respectively.
We can summerize the NDP (Neighbour Discovery Protocol) MAC Address resolution process in two steps as shown below.
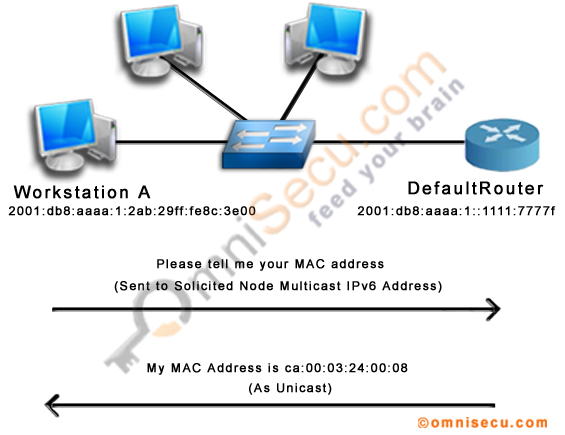
"Workstation A" configured with a Global Unicast IPv6 address 2001:db8:aaaa:1:2ab:29ff:fe8c:3e00/64, wants to resolve the MAC address of the default gateway interface, configured with Global Unicast IPv6 address 2001:db8:aaaa:1::1111:777f/64.
Step 1) "Workstation A" initiates the process by sending a NDP (Neighbour Discovery Protocol) Neighbour Solicitation Message, with a Solicited Node IPv6 Multicast address as the destination address. Click the following link to learn more about Solicited Node IPv6 Multicast addresses.
Step 2) After receiving the NDP (Neighbour Discovery Protocol) Neighbour Solicitation Message, the router will send back an NDP (Neighbour Discovery Protocol) Neighbour Advertisement Message as Unicast, which contains the link-layer address (MAC Address) of the corresponding IPv6 Address.
NDP (Neighbour Discovery Protocol) Neighbour Solicitation (NS)
NDP (Neighbour Discovery Protocol) Neighbor solicitation messages are sent by an IPv6 device to resolve the link-layer address (MAC Address) of another IPv6 device. The source IPv6 address in a NDP (Neighbour Discovery Protocol) Neighbor Solicitation message is the IPv6 address of the corresponding interface in the local-link. The destination address in a NDP (Neighbour Discovery Protocol) Neighbor solicitation message is the Solicited-Node IPv6 Multicast address.
The format for NDP (Neighbour Discovery Protocol) Neighbour Solicitation (NS) message is shown below.

Following screen shot is a Wireshark capture of NDP (Neighbour Discovery Protocol) Neighbour Solicitation message.
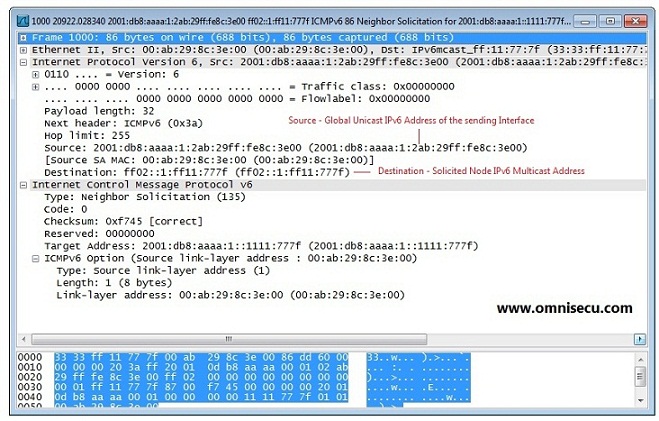
Following table provides more information about NDP (Neighbour Discovery Protocol) Neighbour Solicitation message fields.
| NDP Neighbour Solicitation Message fields | Description |
|---|---|
| Source Address | Unicast Address of the sending interface |
| Destination Address | Destination Address field is set to the Solicited Node Multicast IPv6 address of the target interface |
| Type | The Type field in NDP (Neighbour Discovery Protocol) Neighbour Solicitation message contains the Type value for Neighbour Solicitation message, which is 135. |
| Code | The Code field in NDP (Neighbour Discovery Protocol) Neighbour Solicitation message contains the Code value, which is 0. |
| Checksum | ICMPv6 Checksum Value |
| Reserved | Reserved for future use (32 bits) |
| Source Link-layer Address | Source Link-layer field contains the Link-Layer Address (MAC address) of the sender. This field is used by the IPv6 device to determine the unicast MAC address of the host who sent the Neighbour Solicitation message. Neighbour Advertisement message (which is a response to Neighbour Solicitation message) will be sent back to this MAC address. |
NDP (Neighbour Discovery Protocol) Neighbour Advertisement (NA)
NDP (Neighbour Discovery Protocol) Neighbour Advertisement messages can be Solicited or Unsolicited. Solicited Neighbour Advertisement messages are response messages to a Neighbour Solicitation message sent from another IPv6 device. Unsolicited Neighbour Advertisement messages are sent from an IPv6 device when there is a change in the link-layer address of an interface, with the destination address as All-nodes IPv6 multicast address (FF02::1). Every IPv6 devices will process this message, because every IPv6 devices in the link have joined to All-nodes IPv6 multicast address.
NDP (Neighbour Discovery Protocol) Neighbour Advertisement (NA) message format is shown below.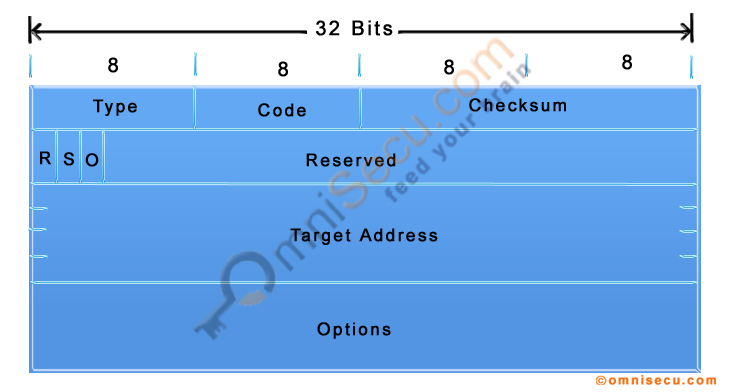
Following screen shot is a Wireshark capture of NDP (Neighbour Discovery Protocol) Neighbour Advertisement (NA) message.
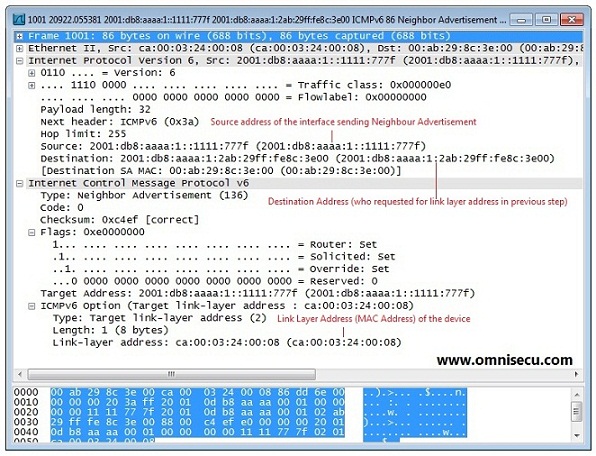
Following table provides more information about NDP (Neighbour Discovery Protocol) Neighbour Advertisement message fields.
| NDP Neighbour Advertisement Message fields | Description |
|---|---|
| Source Address | Unicast Address of the sending interface |
| Destination Address | For solicited Neighbour Advertisement, this field is set to Unicast IPv6 address of the interface which sent the NDP (Neighbour Discovery Protocol) Neighbaour Solicitation message previously. For unsolicited Neighbour Advertisement, this field is set to All Nodes Multicast IPv6 Address (FF02::1). |
| Type | The Type field in NDP (Neighbour Discovery Protocol) Neighbour Advertisement message message contains the Type value for Neighbour Advertisement message, which is 136. |
| Code | The Code field in NDP (Neighbour Discovery Protocol) Neighbour Advertisement message contains the Code value, which is 0. |
| Checksum | ICMPv6 Checksum Value |
| Flags | Three Flags in NDP (Neighbour Discovery Protocol) Neighbour Advertisement message are Router, Solicited and Override. Router: Set to 1, if the sender is a Router Solicited: Set to 1, if Neighbour Advertisement is a response to Neighbour Solicitation message. Override: Used to tell the receiving device that it must override the link-layer address in the existing neighbor cache (when set to 1). |
| Target Address | The Target Address field contains the solicited IPv6 address for solicited Neighbour Advertisement or the IPv6 address of the interface which the device want to advertise for unsolicited Neighbour advertisement. |
| Target Link-layer Address (ICMPv6 Options) | Target Link-layer Address contains the MAC address of the solicited IPv6 address |
Written by Jajish Thomas. Last updated on 19th May, 2024.