Introduction to Auditing in Windows 2003
Auditing is specifically designed into most features in Windows Server 2003.
Auditing waits for a specific event to occur, and then reports on it within the Event Viewer. Auditing events in Windows 2003 can be divided into two types and they are success events and failure events. Auditing can be used for user logon/logoff events and file access events. Auditing can be turned on through a Audit Policy, which is a part of Group Policy.
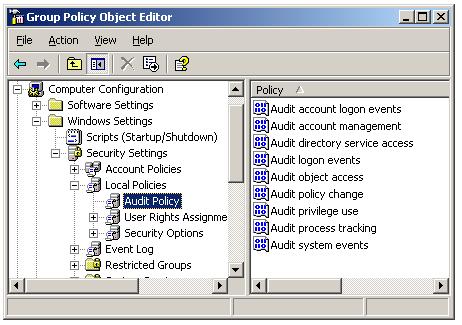
There arenine auditing settings that can be configured on Windows 2003 computer
Audit Account Logon Events: Tracks user logon and logoff events.
Audit Account Management: Reports changes to user accounts
Audit Directory Service Access: Reports access and changes to the directory service.
Audit Logon Events: Reports user logging in and logging off or making a network connection to the computer configured to audit logon events.
Audit Object Access: Reports file and folder access.
Audit Policy Change: Reports changes to group policies
Audit privilege use: Reports events that is related to a user performing a task that is controlled by a user right.
Audit process tracking: Reports events that is related to processes running on the computer.
Audit System Events: Reports standard system events. Not security related.
Auditing can be configured on Audit Policy, which is a part of Group Policy as shown below. You should select the corresponding GPO according to your requirement.