What is Layer 2 Switching loop
In practical Local Area Networking, it is common that the switches are interconnected for redundancy. When switches are interconnected, the network will not fail completely even one if the connected link fails.
When switches are interconnected for redundancy as shown below, another serious network problem can occur, which is known as Layer 2 Switching loop.
The Layer 2 traffic can be classified as unicast (one to one), multicast (one to many), and broadcast (one to all). Unicasts, Multicasts and Broadcasts are different types of network communication and are required for the normal operation of the network. MAC addresses for broadcast and multicast are given below.
• Broadcast Destination MAC address - FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FFF
• Multicast Destination MAC addresses - 01:00:5E:00:00:00 to 01:00:5E:7F:FF:FF
In case of a broadcast and multicast switch need to forward the Ethernet frame out all its ports.
For unknown destination MAC addresses also, the switch need to forward the packet to all ports (known as flooding) except the source port, to make sure that the Ethernet frame reach the destination.
To understand Layer 2 Switching loop, refer the following diagram.
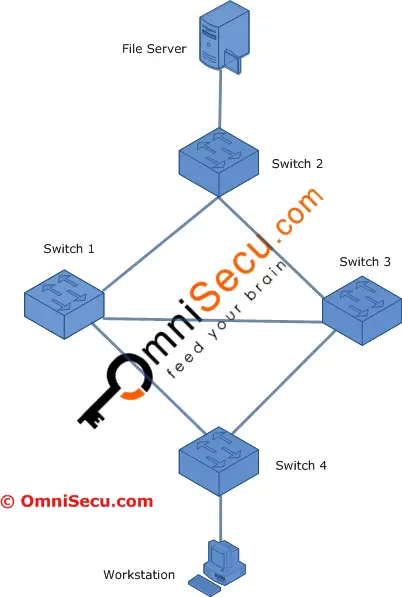
A Ethernet frame originating from Workstation to the File Server, first reaches the Switch 4. Switch 4 will forward the packet to all its ports (except the source port) since the MAC address of the destination device (File Server) may not be available in its MAC address table (File Server is attached to Switch 2).
Both Switch 1 and Switch 3 will receive a copy of the Ethernet frame . Now the Switch 1 and Switch 3 will search for the destination MAC address in its MAC address table and if they fail to find the destination MAC address in their MAC address tables, both the Switches will forward the Ethernet frame to all the ports (except the source port). This may cause the Ethernet frame to reach back the Switch 4 via path Switch 1 – Switch 3 – Switch 4 or Switch 3 – Switch 1 – Switch 4. This may lead to a switching loop and the Ethernet frame will start circulating the network in a loop.
Another problem is that the File Server can receive multiple copies of the same Ethernet frame arriving via different paths, which leads to additional overhead.
Layer 2 Switching loops may cause serious problem to network performance. Layer 2 Switching loops are prevented in networks using Spanning Tree Protocol.