How Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) select Designated Port
Spanning Tree Designated Port Selection is almost same as Spanning Tree Root Port selection.
After selecting the Spanning Tree Root Ports (best port to reach the Root Bridge), Spanning Tree Protocol will make the other end of the Root Port connecting to the next Switch as Designated Port.
Every Switch has only one Spanning Tree Root Port (best port to reach the Root Switch (Root Bridge)). For any other network segments in a Switch which does not include a Root Port, Spanning Tree will select one port as Desingated Port and other as Non-Designaged Port. For that segment, Designated Port will be in Spanning Tree Forwarding State and Spanning Tree Non-Designated port will be in Spanning Tree Blocking State.
Root Port is the port on any Non-Root Bridge which is the best port to reach the Root Switch (Root Bridge). Hence, there is no Root Port in Root Bridge. All the ports in a Root Switch (Root Bridge) are Spanning Tree Designated Ports and will be in Spanning Tree Forwarding State.
Following are the different steps for selecting the Spanning Tree Designated Port.
• Select the port on the Switch on the network segment (which does not include a Root Port) with the lowest accumulated Spanning Tree Path Cost to the Spanning Root Bridge (Root Switch) as the Designated Port and other side of the Designated Port will be the Non-Designated Port.
• If there is a tie in accumulated Path Costs between the two switches in the network segment, then select the port on the switch with the lowest Spanning Tree Switch ID as the Designated Port and other side of the Designated Port as the Non-Designated Port.
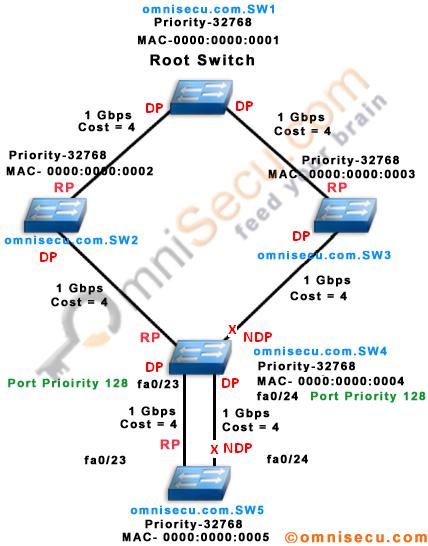
Above topology, the ports marked with "RP" are Spanning Tree Root Ports, the ports marked with "DP" are Designated Ports and the ports marked with "NDP" are Non-Designated Ports. We can see that there is no Spanning Tree Root Port for the network segment between omnisecu.com.SW3 and omnisecu.com.SW4. The port on the Switch which has better Spanning Tree Path Cost (omnisecu.com.SW3) is selected as the Designated port and other end of the Designated Port is the Non-Designated Port.
Spanning Tree Root Port and Spanning TreeSpanning Tree Designated Port will be in Spanning Tree Forwarding State and Non-Designated Port will be in Spanning Tree Blocking State.