Unicast, Multicast and Anycast - Types of communication in IPv6
If you remember the lessons learned in IPv4 topics, the types of network communication in IPv4 are Unicast, Multicast and Broadcast. There is no broadcast in IPv6. The types of network communication in IPv6 are Unicast, Multicast and Anycast.
Read the below contents to know more about Unicast, Multicast and Anycast in IPv6.
What is Unicast?
Unicast is a type of communication where data is sent from one computer to another computer. Unicast is a one-to-one type of network communication. Different data streams are generated for each Unicast connection. This type of communication is the option when clients need different data from network server.
In Unicast type of communication, there is only one sender, and only one receiver.
Examples for IPv6 Unicast type of network communication are
1) Browsing a website. (Web Server is the sender and your computer is the receiver).
2) Downloading a file from a FTP Server. (FTP Server is the sender and your computer is the receiver).
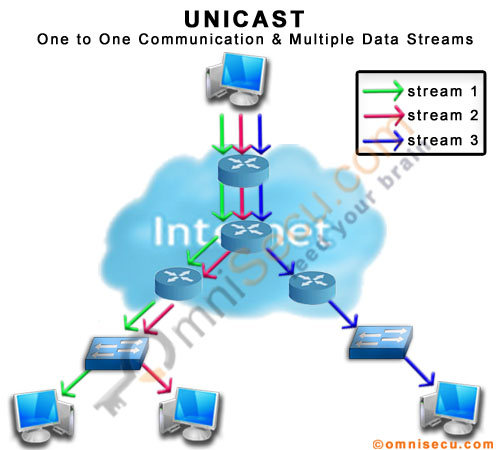
IPv6 Unicast Network Communication
As you can see from the above picture, different data streams are created for different clients in IPv6 Unicast type of communication.
What is Multicast?
Multicast is a type of communication where multicast traffic addressed for a group of devices on the network. IPv6 multicast traffic are sent to a group and only members of that group receive the Multicast traffic.
Devices which are interested in a particular Multicast traffic must join to that Multicast group to receive the traffic. IPv6 Multicast Groups are identified by IPv6 Multicast Addresses.
In Multicast, the sender transmit only one copy of data and it is delivered to many devices (Not all devices as in IPv4 Broadcast) who are interested in that traffic.
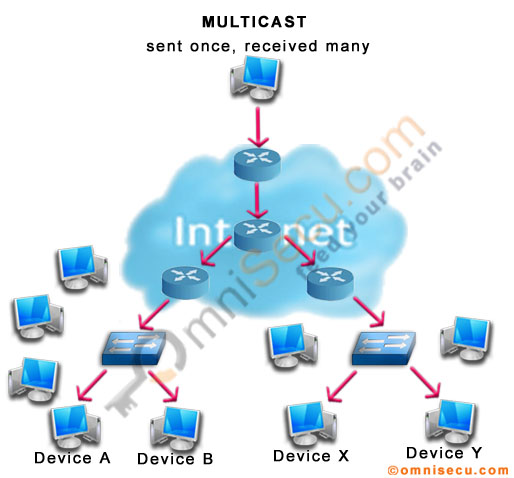
IPv6 Unicast Network Communication
As you can see from the above picture, when multiple clients require same data at the same instance (for example, online TV) we can use multicast instead of unicast. The multicast server generates only one stream of data and that stream is replicated to different devices, who are interested in that data traffic.
Multicast type of network communication can save precious network bandwidth and also network device processor utilization. Refer the below link to know more about IPv6 multicast addresses.
What is Anycast?
Anycast is a type of IPv6 network communication in which IPv6 datagrams from a source of IPv6 traffic are routed to the nearest device (in terms of routing distance) which provide the same service. Every node which provides the same service are configured with same Anycast destination address.
An Anycast IPv6 address can be assigned to different interfaces of different hosts. An IPv6 datagram sent to that Anycast address is delivered to the nearest interface configured with that IPv6 Anycast address, with the help of routing protocols.
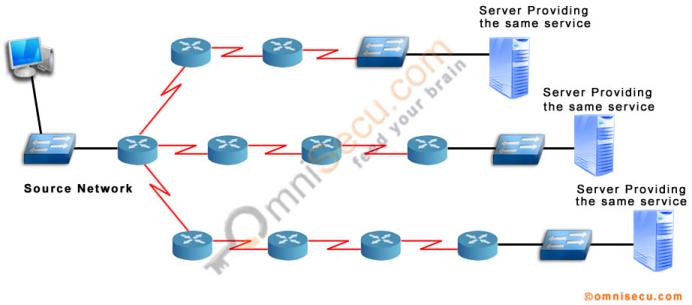
IPv6 Anycast Network Communication
Refer the above image. Here we have three servers providing the same network service, but located at different routing distances from the source network. With the help of routing protocols, IPv6 Anycast network communication can identify the near node from a group of server nodes, which provides the same service and avail the service from the near server.
Written by Jajish Thomas. Last updated on 14th May, 2024.