How SLAAC works in IPv6
SLAAC stands for Stateless Address Auto-configuration. SLAAC allows IPv6 interfaces to automatically configure a unique IPv6 address, without any external intervention. SLAAC is called as stateless, because no server keeps track of IPv6 addresses leased, related MAC address or the lease period duration. This lesson explains how SLAAC works in IPv6.
Please visit following lesson to know What is SLAAC - Stateless Address Auto-configuration in IPv6.
Please note that, by default, EUI-64 based IPv6 addresses are not used in new Windows Operating Systems for obvious security reasons. When EUI-64 based IPv6 addresses are used, an attacker can easily extract the MAC address of the computer from EUI-64 based IPv6 address and that is clearly a security vulnerability.
When SLAAC is used, new Windows Operating Systems generate an IPv6 address with Random Interface ID.
Before starting, let us check the MAC address of the interfaces in our IPv6 client computer.
Following image shows the "getmac" command output from our IPv6 client computer. There are two network interfaces and we are using the first one.
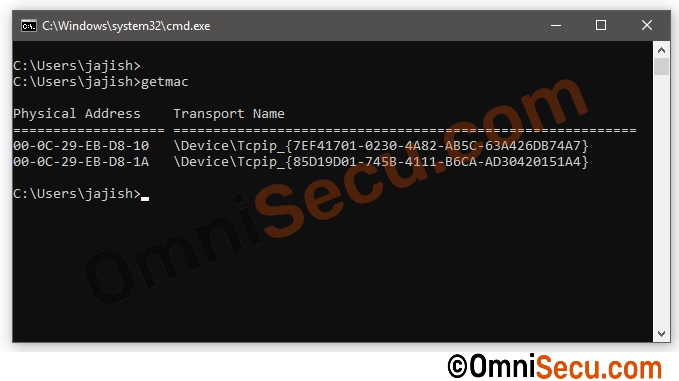
To make sure EUI-64 based IPv6 addresses are not used in new Windows Operating systems (Windows 10 or Windows 11), let us use "ipconfig" command to find the auto-generated link-local IPv6 address of the interface.
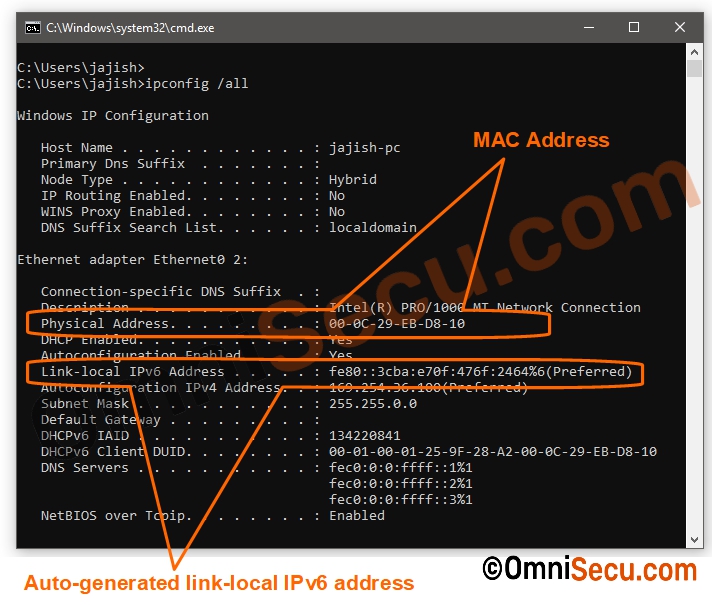
From the above screenshot of "ipconfig" command output, it is clear that the IPv6 link-local address is randomly generated one and not a EUI-64 based IPv6 address.
We assume that above steps are already completed and the network interface is already configured with an auto-configured link-local IPv6 address.
If you have any doubt in above mentioned topics, click the following links to learn more about auto-configured link-local IPv6 address and EUI-64 based IPv6 addresses. Let us proceed further.
Network topology for IPv6 SLAAC lesson
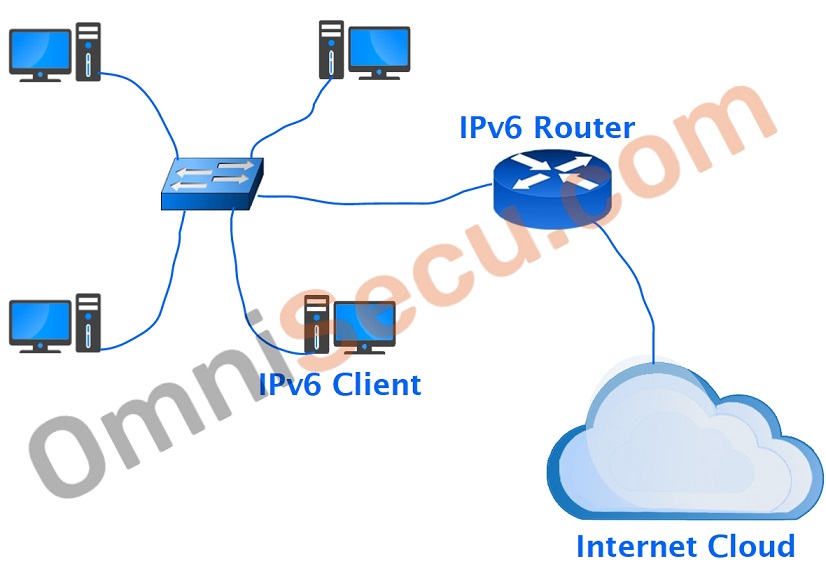
Different steps involved in generating a SLAAC IPv6 address
Step 1 - IPv6 Client sends a Router Solicitation (RS) message.
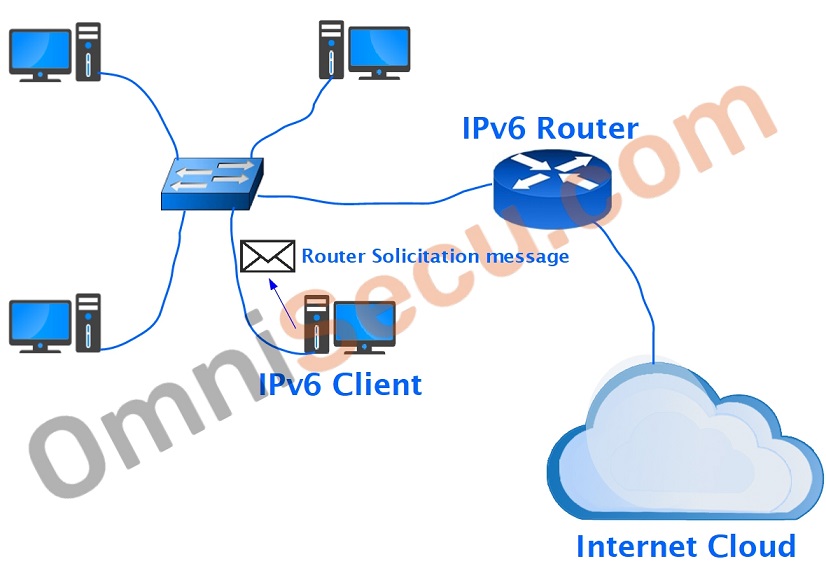
The destination IPv6 multicast address of this Router Solicitation (RS) message is FF02::02, which is addressed to all routers in the local LAN segment. Router Solicitation (RS) message one of the ICMPv6 message types. Only the routing capable devices listen to the messages sent to IPv6 multicast address FF02::02, and all other devices simply discard those Router Solicitation (RS) messages. The purpose of Router Solicitation (RS) message from IPv6 Client is for seeking IPv6 Global unicast address prefix from any IPv6 routing capable router in the LAN segment. Once the IPv6 Global unicast address prefix is received from the IPv6 Router, the client can auto-generate a SLAAC based unique IPv6 global unicast address.
Following image shows the Wireshark capture of Router Solicitation (RS) sent from IPv6 Client.
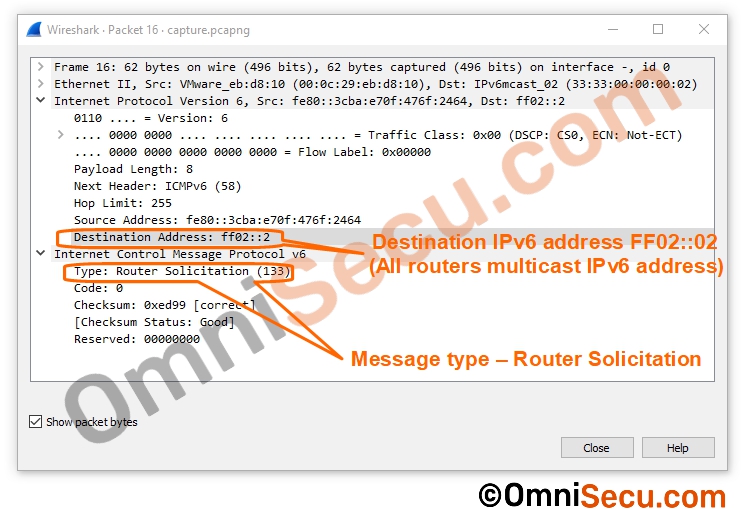
Step 2 - Once the IPv6 router receives Router Solicitation (RS) message, it replies back with an ICMPv6 Router Advertisement (RA) message. The Router Advertisement (RA) message contains the IPv6 prefix and the prefix length.
Following image shows the Wireshark capture of Router Advertisement (RA) sent from IPv6 Router.
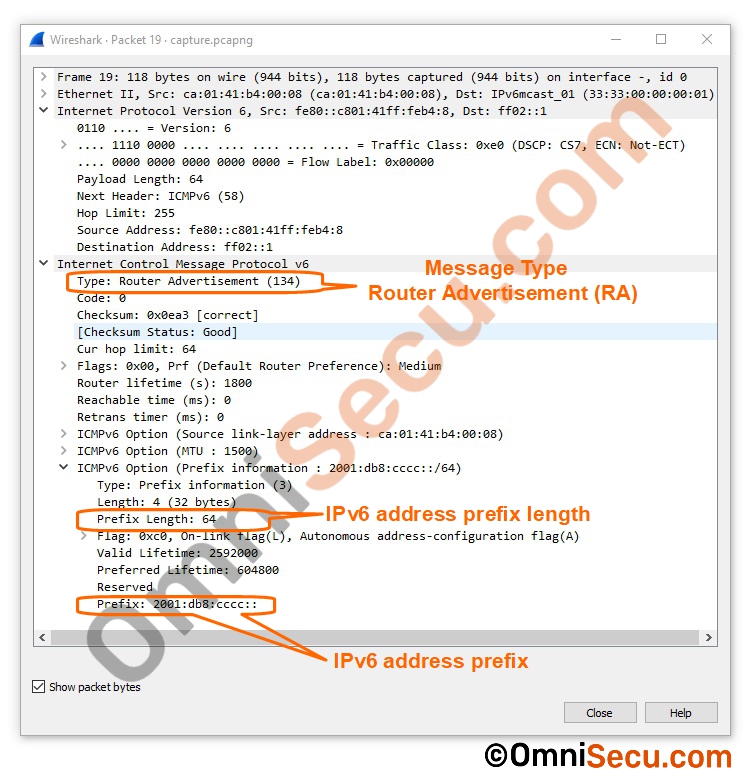
Once the Router Advertisement (RA) from IPv6 Router is received by the client, it will perform a Duplicate Address Detection. If there is no duplicate IPv6 address in the subnet, it will generate and configure itself with a unique IPv6 Global Unicast address, belongs to the same subnet of the IPv6 Router, based on the IPv6 prefix and prefix length received from the IPv6 Router.
Now the IPv6 Client has generated an IPv6 Global Unicast address, using the SLAAC process, that is Stateless Address Auto-configuration.
Step 3 - Now we need to enable SLAAC (Stateless Address Auto-configuration) in the IPv6 Router.
Following commands can be used to enable SLAAC (Stateless Address Auto-configuration) in a Cisco Router. First step is to configure a Global Unicast IPv6 address in the corresponding router interface.
OmniSecuR1# OmniSecuR1#configure terminal OmniSecuR1(config)#interface gigabitEthernet 0/0 OmniSecuR1(config-if)#ipv6 address 2001:db8:aaaa::1/64 OmniSecuR1(config-if)#no shutdown OmniSecuR1(config-if)#exit OmniSecuR1(config)#exit OmniSecuR1#
To enable SLAAC (Stateless Address Auto-configuration), enable IPv6 routing in the IPv6 Router.
OmniSecuR1# OmniSecuR1#configure terminal OmniSecuR1(config)#interface gigabitEthernet 0/0 OmniSecuR1(config-if)#ipv6 unicast-routing OmniSecuR1(config-if)#exit OmniSecuR1(config)#exit OmniSecuR1#
Written by Jajish Thomas. Last updated on 17th May, 2024.