Different methods to assign a Global Unicast IPv6 address to an interface
In IPv6, a network interface must be configured with following important IPv6 configuration settings for internet communication.
• A Global Unicast IPv6 Address
• IPv6 Address subnet prefix length
• Default Router IPv6 address
• DNS Server IPv6 address
In IPv6, we have different methods to assign an IPv6 Global Unicast Address to a network interface. We can assign Global Unicast IPv6 Address to a network interface using the following methods.
Configuring IPv6 Global Unicast Address using Stateful DHCPv6
Similar to DHCP in IPv4, IPv6 network interfaces can also be configured with an IPv6 address, Prefix length, IPv6 address of the default gateway, and the DNS IPv6 address using IPv6 stateful DHCP.
Some important differences between DHCPv4 and DHCPv6 are
1) IPv4 DHCP, DHCP client uses limited broadcast IPv4 address (255.255.255.255) to discover DHCP Server. DHCPv6 clients uses IPv6 DHCP servers and relay agents IPv6 Multicast Address (ff02::1:2) to discover DHCP Server.
2) IPv4 DHCP provide the default router information the DHCP clients. DHCPv6 does not provide the default router information. DHCPv6 servers just rely NDP (Neighbor Discovery Protocol) messages between DHCPV6 clients and routers.
Note that there are changes in names and formats between DHCPv4 messages and DHCPv6 messages. But the basic process of leasing an IP address remains the same.
Configuring IPv6 Global Unicast Address using Stateless Autoconfiguration
IPv6 has a new IPv6 address configuration feature called Stateless Auto-configuration. IPv6 Stateless Autoconfiguration allows a network interface to automatically learn the IPv6 Network Prefix, IPv6 Prefix Length, default router IPv6 address and DNSv6 server addresses. There are different processes to obtain all the above mentioned TCP/IPv6 configuration parameters.
IPv6 uses the Router Solicitation and Router Advertisement messages to learn the IPv6 Network Prefix, IPv6 Prefix Length, default router IPv6 address from network routers. After obtaining the IPv6 Network Prefix, IPv6 Prefix Length, default router IPv6 address from network routers. IPv6 network interfaces can automatically generate a Global Unicast IPv6 Address. IPv6 hosts can generate a unique IPv6 address by combining the network prefix and the interface identifier. IPv6 can use Stateless DHCPv6 to learn the DNS Server’s IPv6 addresses.
Static IPv6 Global Unicast Address Configuration
Similar to IPv4, you can configure Static IPv6 addresses (Manual IPv6 Global Unicast Address Configuration) for network interfaces. You may type-in the entire 128-bit IPv6 address for the network interface, as shown in below image.
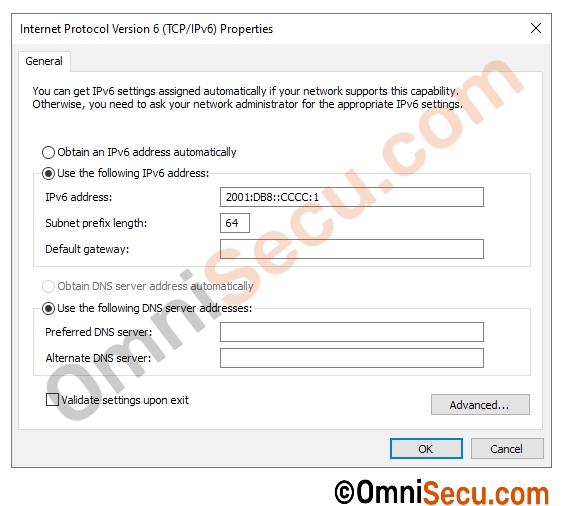
Above image is of a Windows 2022 Server IPv6 settings configuration window. You can see that there are textboxes to configure IPv6 address, Subnet prefix length, Default gateway, Preferred DNS server and Alternate DNS server. You can configure your required IPv6 settings manually in this window. This method is almost similar to static IPv4 address configuration.
Other TCP/IP network configuration information required (default router, DNS Server IPv6 Address) can be configured by typing-in the details or by using Neighbor Discovery Protocol (NDP). Default router information can be obtained using Router Solicitation and Router Advertisement messages and DNS Server IPv6 Address can be obtained using Stateless DHCPv6.
Click the following links to learn how to configure Static Global Unicast IPv6 Address in a Cisco Router Interface and how to configure EUI-64 based Global Unicast IPv6 Address in a Cisco Router Interface.
Written by Jajish Thomas. Last updated on 17th May, 2024.