Comparison between IPv4 Header and IPv6 Header
There are many significant differences between IPv4 header and IPv6 header. Following images are of IPv4 header and IPv6 header format, respectively.
IPv4 header
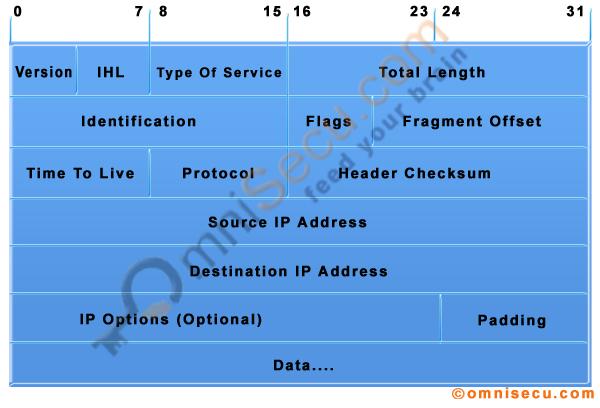
IPv4 Datagram Header
IPv6 header
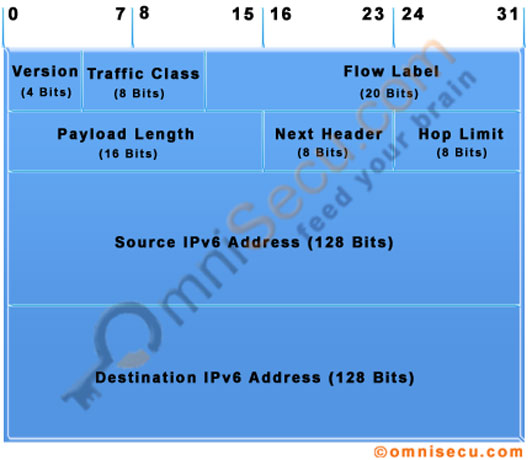
IPv6 Datagram Header
Following are the main differences and comparison between IPv4 header and IPv6 header.
• IPv6 header is much simpler than IPv4 header.
• The size of IPv6 header is fixed 40 bytes. The size of IPv4 header can be between 20 to 60 bytes.
• IPv4 addresses are 32-bit binary numbers (represented in decimal number system) and IPv6 addresses are 128-bit binary numbers (represented in hexadecimal number system).
• IPv4 addresses are represented in decimal number system. IPv6 addresses are represented in hexadecimal number system.
• In IPv4 header, the source and destination IPv4 addresses are 32-bit binary numbers. In IPv6 header, the source and destination IPv6 addresses are 128-bit binary numbers.
• IPv4 header includes space for IPv4 options. In IPv6 header, we have a similar feature known as extension header. IPv4 datagram headers are normally 20-byte in length. But we can include IPv4 option values also along with an IPv4 header. In IPv6 header we do not have options, but have extension headers.
• The fields in the IPv4 header such as IHL (Internet Header Length), identification, flags are not present in IPv6 header.
• Time-to-Live (TTL), a field in IPv4 header, typically used for preventing routing loops, is renamed to its exact meaning, "Hop Limit".
Written by Jajish Thomas. Last updated on 14th May, 2024.