Internet Control Message Protocol, ICMP, How ICMP Work, ICMP Header, ICMP Message Header
Internet Control Message Protocol Version 4 (ICMPv4) is an integral protocol in the TCP/IP protocol suite. Internet Control Message Protocol Version 4 (ICMPv4) was originally published as RFC 777, and later updated by RFC 792. RFC 792 has been updated by RFC 4884, RFC 6633, RFC 6918 etc.
When you send data from one device to another remote device, the IPv4 datagram often travels through one or more routers. There can be errors at routers while they try to forward the IPv4 Datagram to its final destination. Internet Control Message Protocol Version 4 (ICMPv4) protocol is used to report problems with delivery of IPv4 datagrams within an IPv4 network. ICMP is also used for other diagnosis and troubleshooting functions. ICMP messages are used to communicate information like destination network unreachable, better route is available, transmission errors, network congestion issues, time synchronization etc., between network devices.
ICMP uses different messages to return information to sending computers, about routes traveled, reachability issues, route congestion issues, delivery issues etc of an IPv4 datagram. Even though ICMP is encapsulated within IPv4 datagram, ICMP is considered as a Network layer protocol.
The most common ICMP messages
ICMP Echo Request and Echo Reply message : ICMP is often used during test the connectivity between devices. We can use the ping (Packet InterNet Grouper, a command-line utility used to check the connectivity between two devices) command to check connectivity from one device with another device and the ping command is using Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP). Ping command sends an IP datagram packet to the IPv4 address of the device we are trying to check the connectivity and requests the destination device to return the data sent in a response datagram. Ping command uses ICMP Echo Request and Echo Reply.
ICMP Redirect message : ICMP redirect type of messages allows a router on a nonoptimal route between sender and receiver to redirect traffic through a better path via another router.
ICMP Source Quench message : If a device is sending large amounts of data to another remote device, the volume can flood the router with data. The router can use ICMP to send a Source Quench message to the source IPv4 address to ask it to slow down the rate at which it is sending data. Source Quench is deprecated.
ICMP Destination Unreachable message : If a router receives a datagram that cannot be delivered, Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) returns a Destination Unreachable message to the source IPv4 address.
ICMP Time Exceeded message : Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) sends this message to the source IP if an IPv4 datagram is discarded because Time-to-Live (TTL) value reaches zero. One reason is the destination device is too many router hops away to reach with the current Time-to-Live (TTL) value or a routing loop (An undesirable condition when the IP Datagrams loop infinitely between the routers, without reaching the destination).
ICMP Router Advertisement and Router Solicitation messages : ICMP Router Advertisement and Router Solicitation messages allows routers to advertise their presence in a network segment and for computers to discover routers.
Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) Message Header
An ICMP header follows the IPv4 datagram header. The value "1" in 8-bit "Protocol" field in an IPv4 datagram header indicates that the ICMP header follows the IPv4 datagram header.
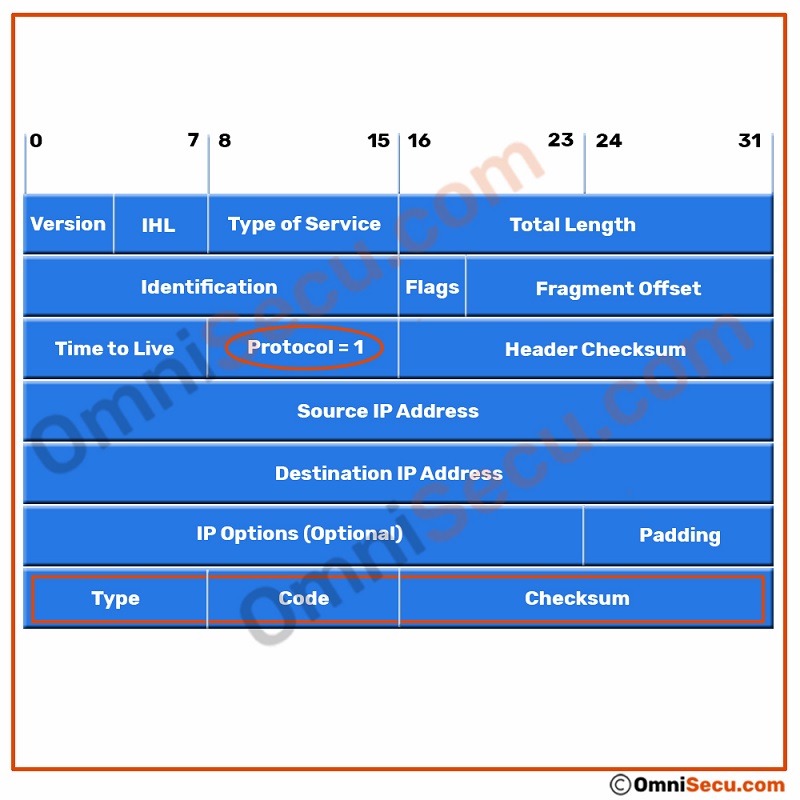
ICMP header has two parts. The first four bytes are available for all types of ICMP messages. The first four bytes contains "Type", "Code" and "Checksum" fields in an ICMP header. First four bytes of ICMP header is shown below.
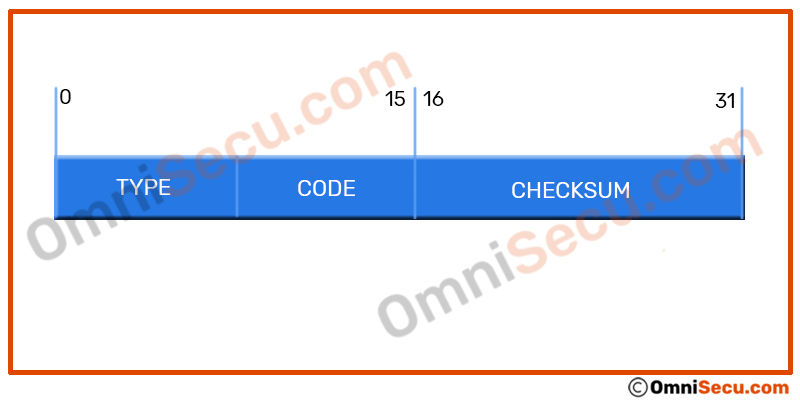
Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) Header
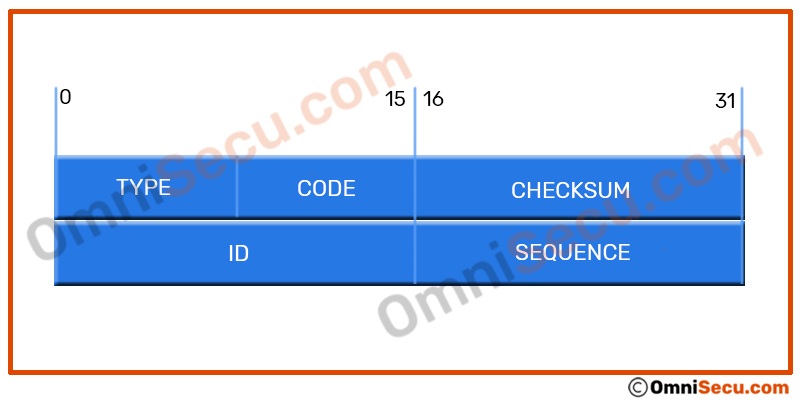
The contents of the remaining part of ICMP packet depends on the ICMP message type. For example; ID (identifier) and SEQUENCE (sequence number) fields are the next four bytes (32 bits) after Type, Code and Checksum fields in an Echo Request and Echo reply ICMP message. Please refer below image.
Type and Code : The following table shows the values which are possible for the Type and Code fields in the Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) header.
ICMP header fields
| Type Number | Code | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 0 - Echo Reply | 0 | Echo reply (used for Ping/Tracert etc) |
| 1 and 2 |
|
Reserved |
| 3 - Destination unreachable | 0 | Destination network unreachable |
| 1 | Destination host unreachable | |
| 2 | Destination protocol unreachable | |
| 3 | Destination port unreachable | |
| 4 | Fragmentation required, and DF set | |
| 5 | Source route failed | |
| 6 | Destination network unknown | |
| 7 | Destination host unknown | |
| 8 | Source host isolated | |
| 9 | Network administratively prohibited | |
| 10 | Host administratively prohibited | |
| 11 | Network unreachable for Type Of Service | |
| 12 | Host unreachable for Type of Service | |
| 13 | Administratively prohibited | |
| 4 - Source Quench | 0 | Traffic Congestion Control |
| 5 - Redirect Message | 0 | Redirect Datagram for the Network |
| 1 | Redirect Datagram for the Host | |
| 2 | Redirect Datagram for the Type of Service & network | |
| 3 | Redirect Datagram for the Type of Service & host | |
| 6 - Alternate Host Address |
|
Alternate Host Address - Deprecated |
| 7 |
|
Reserved |
| 8 - Echo Request | 0 | Echo request |
| 9 - Router Advertisement | 0 | Router Advertisement |
| 10 - Router Solicitation | 0 | Router discovery/selection/solicitation |
| 11 - Time Exceeded | 0 | TTL expired |
| 1 | Fragment reassembly time exceeded | |
| 12 - Parameter Problem | 0 | Pointer indicates the error |
| 1 | Missing a required option | |
| 2 | Bad length | |
| 13 - Timestamp Request | 0 | Timestamp Request |
| 14 - Timestamp Reply | 0 | Timestamp Reply |
| 15 - Information Request | 0 | Information Request |
| 16 - Information Reply | 0 | Information Reply |
| 17 - Address Mask Request | 0 | Address Mask Request |
| 18 - Address Mask Reply | 0 | Address Mask Reply |
| 19 |
|
Reserved for security |
| 20 through 29 |
|
Reserved for robustness experiment |
| 30 | 0 | Information Request |
| 31 |
|
Datagram Conversion Error |
| 32 |
|
Mobile Host Redirect |
| 33 |
|
Where-Are-You |
| 34 |
|
Here-I-Am |
| 35 |
|
Mobile Registration Request |
| 36 |
|
Mobile Registration Reply |
| 37 |
|
Domain Name Request |
| 38 |
|
Domain Name Reply |
| 39 - SKIP Algorithm |
|
SKIP Algorithm Discovery Protocol |
| 40 - Photuris protocol |
|
Photuris (Firefly) security protocol |
| 41 |
|
ICMP for experimental mobility protocols such as Seamoby |
| 42 through 255 |
|
Reserved |
Checksum : The checksum field in the Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) message contains error checking data calculated from the Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) header+data, with value 0 for this field.
ID : The ID field in the Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) message contains an ID value, should be returned in case of ECHO REPLY.
Sequence number : The sequence number field in the Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) message is the sequence number for each host, and is incremented by 1 for each packet.
The ID (identifier) and SEQUENCE (sequence number) are used to associate each echo request with its reply.
You have learned Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP), use of Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP), Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) message header and the fields in Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) message. Click "Next" to continue.