IPv4 Directed broadcast address
Here, in this tutorial lesson we will learn about IPv4 directed broadcast addresses.
Broadcast is a type of network communication in IPv4. In broadcast type of communication, a computer in a network can send an IPv4 datagram packet once and that IPv4 datagram packet will be delivered to all other computers in that network. In other words, broadcast is one to all type of communication. In broadcast, the sender sends the IPv4 datagram packets once and all other computers in the intended destination network receives a copy of that IPv4 datagram packet. There are two types of broadcasts - limited broadcast and directed broadcast. Both limited broadcast and directed broadcast use different special IPv4 addresses as the destination addresses.
Directed broadcast address is a special IPv4 address used as the destination address in IPv4 datagram packet for directed broadcasts.
Directed broadcast address is the last address of an IPv4 address block. Directed broadcast addresses are derived by setting all the host bits in an IPv4 address block as binary number, "1".
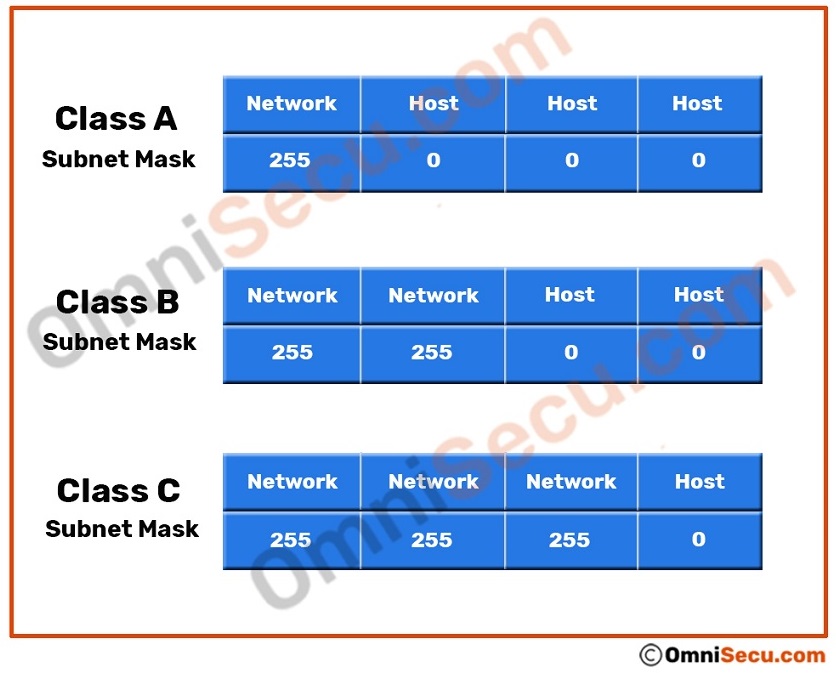
Let’s learn what is directed broadcast address with examples of Class A, Class B and Class C IPv4 networks. Default subnet masks of Class A, Class B and Class C networks are given below.
- For Class A network, the first octet belongs to the network part and remaining three octets belongs to the host part. So, the default subnet mask of a Class A network is 255.0.0.0.
- For Class B network, the first two octets belongs to the network part and remaining two octets belongs to the host part. So, the default subnet mask of a Class B network is 255.255.0.0.
- For Class C network, the first three octets belongs to the network part and remaining one octet belongs to the host part. So, the default subnet mask of a Class B network is 255.255.255.0.
To understand the concept clearly, refer below image.
Remember, directed broadcast address is the last address of an IPv4 address block. Directed broadcast addresses are derived by setting all the host bits as binary number, "1".
Directed broadcast address of a Class A network
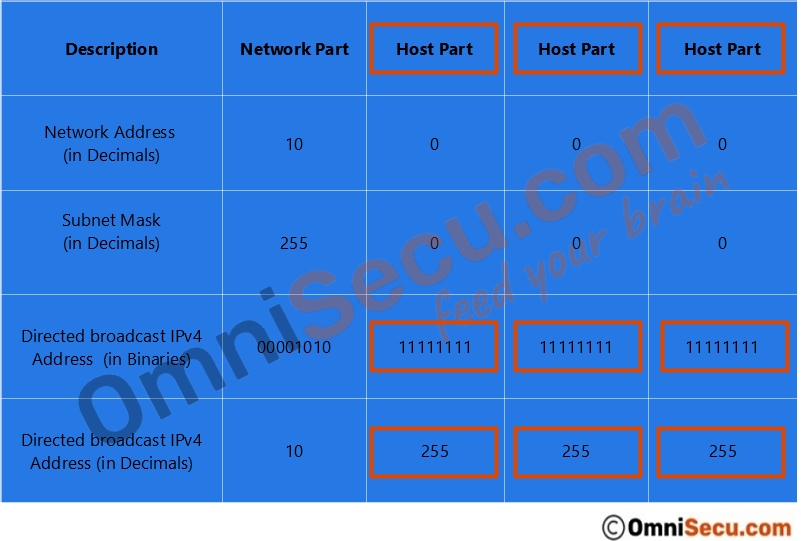
Let us take an example of IPv4 Class A network 10.0.0.0. We have already learned that for Class A network, first octet belongs to the network part and remaining three octets belongs to the host part. So, the default subnet mask of a Class A network is 255.0.0.0.
If we keep all the host bits of 10.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 network as binary number "1", we get the IPv4 directed broadcast address of 10.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 network as 10.255.255.255. Please refer below image.
Directed broadcast address of a Class B network
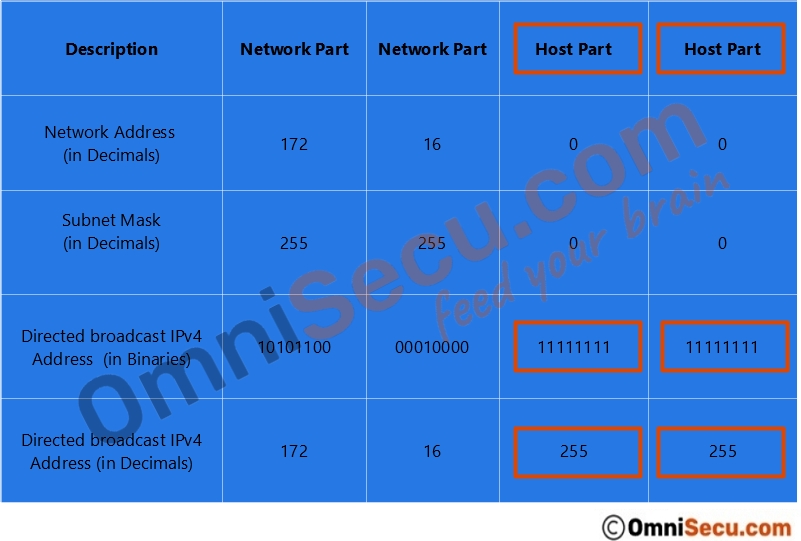
Let us take an example of IPv4 Class B network 172.16.0.0. We have already learned that for Class B network, first two octets belongs to network part and remaining two octets belongs to host part. So, the default subnet mask of a Class B network is 255.255.0.0.
If we keep all the host bits of 172.16.0.0 255.255.0.0 network as binary number "1", we get the IPv4 directed broadcast address of 172.16.0.0 255.255.0.0 network as 172.16.255.255. Please refer below image.
Directed broadcast address of a Class C network
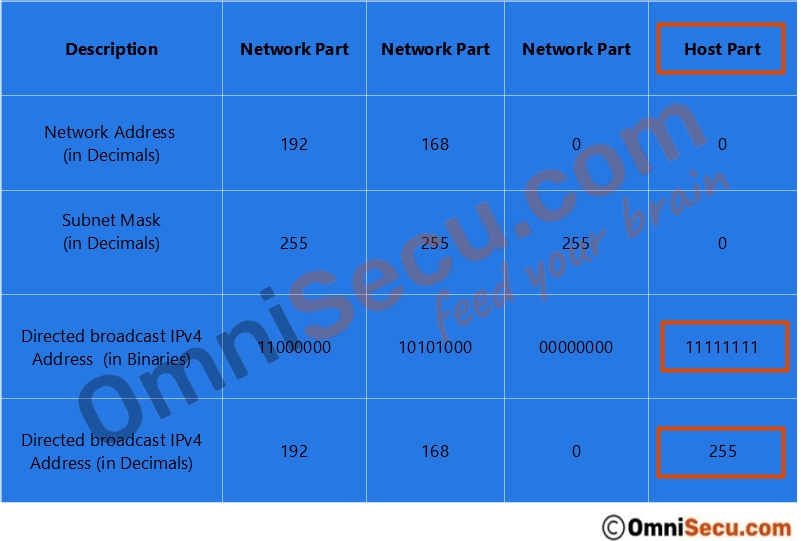
Let us take an example of IPv4 Class C network 192.168.0.0. We have already learned that for Class C network, the first three octets belongs to network part and remaining one octet belongs to host part. So, the default subnet mask of a Class B network is 255.255.255.0.
If we keep all the host bits of 192.168.0.0 255.255.255.0 network as binary number "1", we get the IPv4 directed broadcast address of 192.168.0.0 255.255.255.0 network as 192.168.0.255. Please refer below image.
You cannot use a directed broadcast IPv4 address as an IPv4 address for a network device.