Windows 2003 Certificate Server Architecture
The following figure illustrates the Microsoft Windows 2003 Certificate Server Architecture.
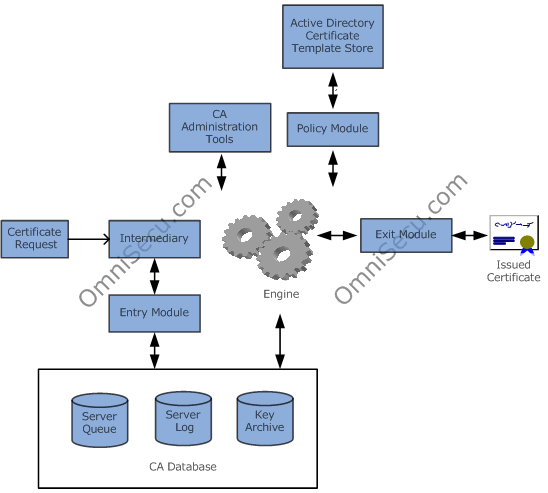
Microsoft Windows 2003 Certificate Server engine is certsrv.exe. The engine has three important modules to which the Certificate Server engine communicates. They are 1) Entry Module 2) Policy Module and 3) Exit Module.
Entry Module: The entry module accepts PKCS10 and CMC formatted certificate requests. The Entry Module place the certificate requests in a queue for policy module.
Policy Module: A policy module is a set of instructions that tells the CA what to do with incoming certificate requests. A policy module can automatically approve a request, reject a request, or mark a request as pending for an administrator to manually approve it based on any criteria coded into the module.
Exit Module: An exit module allows the CA to take some action after a certificate is generated. For example, an exit module might publish new certificates in the Active Directory or export them to the file system.
The exit and policy modules are both customizable and replaceable. If the policy module or the exit module does not match to the needs of an organization, it can develop modules in C++ or Visual Basic (VB) and plug them into the CA architecture.
The Certificate Server has a database which is used to store certificate transactions and status information, certificates, and optionally archived private keys. The database (<CAName>.edb) is by default located in the system32\certlog folder. The Certificate Server engine communicates with its database through the certdb.dll.
The GUI administrative tool used for managing the certificate server is "Certificate Authority" MMC snap-in. It can be located inside Administrative Tools. Windows 2003 also has a command line tool to manage the certificate server and this tool is certutil.exe.
An intermediary or Registration Authorities (RAs) are applications that help the client in generating correctly formatted PKCS10 or CMC certificate request files. Examples of Windows Server 2003 intermediaries are the Web enrollment pages (works using HTTP) and the MMC Certificates snap-in (works using RPC) intermediary.