Certificate Authority (CA) Hierarchy, Root CA, Intermediate CA, Issuing CA
Digital certificates created by a Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) Certificate Authority (CA) are verified using a chain of trust. The trust anchor for the digital certificate is the Root Certificate Authority (CA), and any Certificate Authority (CA) which comes under Root Certificate Authority (Root CA) is known as a subordinate Certificate Authority (CA). The following figure shows the Certificate Authority Hierarchy.
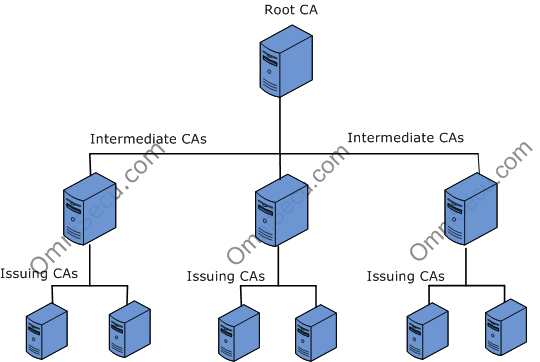
Root CA: A Root CA is the topmost Certificate Authority (CA) in a Certificate Authority (CA) hierarchy. Each Certificate Authority (CA) hierarchy begins with the Root CA, and multiple CAs branch from this Root CA in a parent-child relationship. All child CAs must be certified by the corresponding parent CA back to the Root CA. The Root CA is kept in a secure area and it is usually a stand-alone offline CA (to make it topmost secure Certificate Authority (CA). The root CA provides certificates for intermediate CAs. The certificates can be revoked if they are compromised.
Intermediate CAs: An intermediate Certificate Authority (CA) is a CA that is subordinate to another CA (Root CA or another intermediate CA) and issues certificates to other CAs in the CA hierarchy. Intermediate CAs are usually stand-alone offline CAs like root CAs.
Issuing CAs: Issuing CAs are used to provide certificates to users, computers, and other services. There can be multiple issuing CAs, and one issuing CA can be used for generating computer certificates and another can be used for generating user certificates.