Tunnel Mode - Internet Protocol Security - IPSec
IPSec Tunnel mode is used to secure gateway-to-gateway traffic. IPSec Tunnel mode is used when the final destination of the data packet is different from the security termination point. IPsec Tunnel mode protects the entire contents of the tunneled packets.
As we learned in previous lesson, Transport mode is a good option securing host-to-host communication and Tunnel mode is the option for Virtual Private Network (VPN).
The IPSec Tunnel mode data packets sent from the source device are accepted by the security gateway (a router or a server) and forwarded to the other end of the tunnel, where the original packets are extracted and then forwarded to their final destination device.
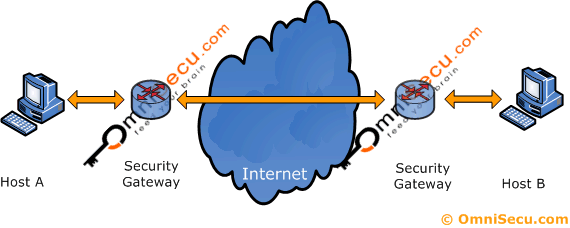
Figure 4: Gateway-to-gateway security using IPSec Tunnel mode
When we use IPSec Tunnel mode, the IP datagram is encapsulated in another IP datagram and an IPSec header is inserted between two IP headers.
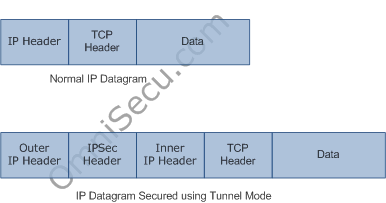
Figure 5: IP Datagram secured using IPSec Tunnel mode.
An IPSec tunneled mode packet has outer IP header and inner IP header. The inner header is the host IP header itself and the outer header is added by the security gateway.